Health-Related Quality of Life and Its Socio-Demographic and Behavioural Correlates during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Estonia
- PMID: 35897422
- PMCID: PMC9331429
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19159060
Health-Related Quality of Life and Its Socio-Demographic and Behavioural Correlates during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Estonia
Abstract
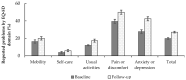
The aim of the study was to analyse health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among the Estonian general population and its socio-demographic and behavioural correlates during the COVID-19 pandemic. Longitudinal data on 1781 individuals from an Estonian rapid-assessment survey on COVID-19 were used. HRQoL was assessed with the EQ-5D-3L in June 2020 (baseline) and in May 2021 (follow-up). The HRQoL index score and its socio-demographic and behavioural variations were analysed using paired t-tests and Tobit regression modelling. Statistically significant declines in mean EQ-5D index scores were observed for all socio-demographic and behavioural variables considered. Most of these changes were due to increased reporting of problems in the pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression health domains. Older age, being unemployed or economically non-active and having financial difficulties were significantly associated with lower HRQoL in both baseline and follow-up measurements. In the follow-up data, women had significantly lower HRQoL compared to men, whereas higher education proved to be the only protective factor regarding HRQoL. Unhealthy dietary habits and low physical activity had a negative impact on the HRQoL score in the follow-up data. These results indicate that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a substantial impact on HRQoL in the Estonian population.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; EQ-5D; Estonia; health behaviour; health-related quality of life; inequalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Listings of WHO’s Response to COVID-19. [(accessed on 8 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline.
-
- Worldometers. [(accessed on 8 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Capasso A., Kim S., Ali S.H., Jones A.M., DiClemente R.J., Tozan Y. Employment conditions as barriers to the adoption of COVID-19 mitigation measures: How the COVID-19 pandemic may be deepening health disparities among low-income earners and essential workers in the United States. BMC Public Health. 2022;22:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13259-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical