Distinct Patterns of GR Transcriptional Regulation in Liver and Muscle of LPS-Challenged Weaning Piglets
- PMID: 35897645
- PMCID: PMC9331734
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158072
Distinct Patterns of GR Transcriptional Regulation in Liver and Muscle of LPS-Challenged Weaning Piglets
Abstract
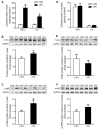
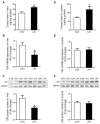
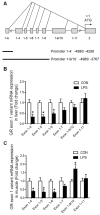
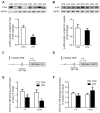
Glucocorticoid receptor (GR), which is ubiquitously expressed in nearly all cell types of various organs, mediates the tissue-specific metabolic and immune responses to maintain homeostasis and ensure survival under stressful conditions or pathological challenges. The neonatal period is metabolically demanding, and piglets are subjected to multiple stressors in modern intensive farms, especially around weaning. The liver is more responsive to LPS challenge compared to muscle, which is indicated by significantly increased TLR4 and p-p65, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels in association with GR down-regulation at both mRNA and protein levels. GR binding to the putative nGRE on TNF-α and IL-6 gene promoters decreased in the liver, but not muscle, upon LPS stimulation. The transcriptional regulation of GR also showed striking differences between liver and muscle. GR exon 1 mRNA variants 1-4, 1-5, and 1-6 were down-regulated in both liver and muscle, but a significant up-regulation of GR exon 1-9/10 mRNA variants abolished the change of total GR mRNA in the muscle in response to LPS stimulation. The significant down-regulation of GR in the liver corresponded with significantly decreased binding of p-GR and diminished histone acetylation in GR gene promoters. These results indicate that tissue-specific GR transcriptional regulation is involved in the differential inflammation responses between liver and muscle.
Keywords: GR; liver; muscle; pig; tissue specificity; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Carrillo-de Sauvage M.A., Maatouk L., Arnoux I., Pasco M., Sanz Diez A., Delahaye M., Herrero M.T., Newman T.A., Calvo C.F., Audinat E., et al. Potent and multiple regulatory actions of microglial glucocorticoid receptors during CNS inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:1546–1557. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

