Effects and Mechanism of Particulate Matter on Tendon Healing Based on Integrated Analysis of DNA Methylation and RNA Sequencing Data in a Rat Model
- PMID: 35897746
- PMCID: PMC9332732
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158170
Effects and Mechanism of Particulate Matter on Tendon Healing Based on Integrated Analysis of DNA Methylation and RNA Sequencing Data in a Rat Model
Abstract
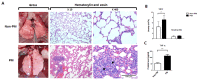
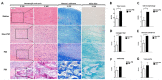
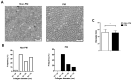
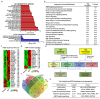
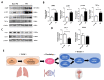
Exposure to particulate matter (PM) has been linked with the severity of various diseases. To date, there is no study on the relationship between PM exposure and tendon healing. Open Achilles tenotomy of 20 rats was performed. The animals were divided into two groups according to exposure to PM: a PM group and a non-PM group. After 6 weeks of PM exposure, the harvest and investigations of lungs, blood samples, and Achilles tendons were performed. Compared to the non-PM group, the white blood cell count and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in the PM group were significantly higher. The Achilles tendons in PM group showed significantly increased inflammatory outcomes. A TEM analysis showed reduced collagen fibrils in the PM group. A biomechanical analysis demonstrated that the load to failure value was lower in the PM group. An upregulation of the gene encoding cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) was detected in the PM group by an integrated analysis of DNA methylation and RNA sequencing data, as confirmed via a Western blot analysis showing significantly elevated levels of phosphorylated CREB. In summary, PM exposure caused a deleterious effect on tendon healing. The molecular data indicate that the action mechanism of PM may be associated with upregulated CREB signaling.
Keywords: Achilles tendon; CREB signaling; DNA methylation; RNA sequencing; particulate matter; rat; tendon healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cells from a hypoxic culture improve and engraft Achilles tendon repair.Am J Sports Med. 2013 May;41(5):1117-25. doi: 10.1177/0363546513480786. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Am J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23539044
-
Gait analysis combined with the expression of TGF-β1, TGF-β3 and CREB during Achilles tendon healing in rat.Chin J Traumatol. 2021 Nov;24(6):360-367. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Chin J Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 34696976 Free PMC article.
-
Repair within the first 48 h in the treatment of acute Achilles tendon ruptures achieves the best biomechanical and histological outcomes.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Sep;28(9):2788-2797. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05536-w. Epub 2019 May 22. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 31119340
-
Investigation of the biomechanical and histopathological effects of autologous conditioned serum on healing of Achilles tendon.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018 May;52(3):226-231. doi: 10.1016/j.aott.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018. PMID: 29454565 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation: A critical epigenetic mechanism underlying the detrimental effects of airborne particulate matter.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Oct;161:173-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.083. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 29883871 Review.
Cited by
-
Up-regulation of CREB-1 regulates tendon adhesion in the injury tendon healing through the CREB-1/TGF-β3 signaling pathway.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Apr 25;24(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06425-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37098516 Free PMC article.
-
An Atelocollagen Injection Enhances the Healing of Nonoperatively Treated Achilles Tendon Tears: An Experimental Study in Rats.Orthop J Sports Med. 2023 Oct 18;11(10):23259671231200933. doi: 10.1177/23259671231200933. eCollection 2023 Oct. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37868218 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in stem cell therapies for achilles tendinopathy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 13;13:1516250. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1516250. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40181824 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kushta J., Paisi N., Van Der Gon H.D., Lelieveld J. Disease burden and excess mortality from coal-fired power plant emissions in Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021;16:045010. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abecff. - DOI
-
- Mukherjee A., Agrawal M. A global perspective of fine particulate matter pollution and its health effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017;244:5–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

