Antitumor Effects of Ral-GTPases Downregulation in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 35897776
- PMCID: PMC9330696
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158199
Antitumor Effects of Ral-GTPases Downregulation in Glioblastoma
Abstract
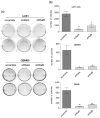
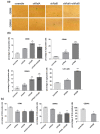
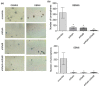
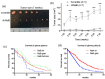
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common tumor in the central nervous system in adults. This neoplasia shows a high capacity of growth and spreading to the surrounding brain tissue, hindering its complete surgical resection. Therefore, the finding of new antitumor therapies for GBM treatment is a priority. We have previously described that cyclin D1-CDK4 promotes GBM dissemination through the activation of the small GTPases RalA and RalB. In this paper, we show that RalB GTPase is upregulated in primary GBM cells. We found that the downregulation of Ral GTPases, mainly RalB, prevents the proliferation of primary GBM cells and triggers a senescence-like response. Moreover, downregulation of RalA and RalB reduces the viability of GBM cells growing as tumorspheres, suggesting a possible role of these GTPases in the survival of GBM stem cells. By using mouse subcutaneous xenografts, we have corroborated the role of RalB in GBM growth in vivo. Finally, we have observed that the knockdown of RalB also inhibits cell growth in temozolomide-resistant GBM cells. Overall, our work shows that GBM cells are especially sensitive to Ral-GTPase availability. Therefore, we propose that the inactivation of Ral-GTPases may be a reliable therapeutic approach to prevent GBM progression and recurrence.
Keywords: Ral-GTPases; RalB; glioblastoma; glioma; recurrence; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ras-related small GTPases RalA and RalB regulate cellular survival after ionizing radiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010 Sep 1;78(1):205-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.03.023. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. PMID: 20619549 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin binds RalA and RalB and is required for the thrombin-induced activation of Ral in human platelets.J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):28972-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201504200. Epub 2002 May 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12034722
-
Genetic deletion of RALA and RALB small GTPases reveals redundant functions in development and tumorigenesis.Curr Biol. 2012 Nov 6;22(21):2063-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.09.013. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 23063435
-
The RAL Enigma: Distinct Roles of RALA and RALB in Cancer.Cells. 2022 May 14;11(10):1645. doi: 10.3390/cells11101645. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35626682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ral GTPases: crucial mediators of exocytosis and tumourigenesis.J Biochem. 2015 May;157(5):285-99. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvv029. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25796063 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic pan-cancer analysis identifies RALA as a tumor targeting immune therapeutic and prognostic marker.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1046044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1046044. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466919 Free PMC article.
-
The RAL Small G Proteins Are Clinically Relevant Targets in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;16(17):3043. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173043. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272901 Free PMC article.
-
RalB promotes lymph node metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Genes Genomics. 2025 Jun;47(6):697-705. doi: 10.1007/s13258-025-01628-9. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Genes Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40208483
-
Impact of IDH Mutations, the 1p/19q Co-Deletion and the G-CIMP Status on Alternative Splicing in Diffuse Gliomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 6;24(12):9825. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129825. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37372972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verhaak R.G.W., Hoadley K.A., Purdom E., Wang V., Qi Y., Wilkerson M.D., Miller C.R., Ding L., Golub T., Mesirov J.P., et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

