Bidentate Donor-Functionalized N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Valuable Ligands for Ruthenium-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation
- PMID: 35897879
- PMCID: PMC9329912
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154703
Bidentate Donor-Functionalized N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Valuable Ligands for Ruthenium-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation
Abstract
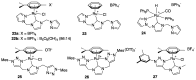
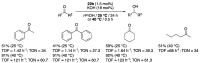
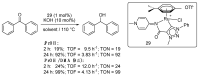
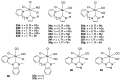
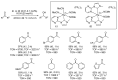
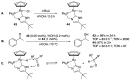
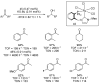
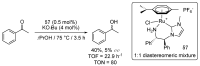
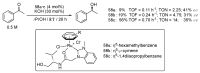
Ruthenium complexes are by far the most studied compounds that catalyze hydrogen transfer reactions. In this review, we describe the use in this field of ruthenium complexes bearing bidentate donor-functionalized N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. The review specifically covers the application in transfer hydrogenations of (k2-CNHC,Y)-ruthenacyclic compounds where the Y donor atom is a N, P, O, or S atom, and where the N-heterocyclic carbene ligand is a classical imidazol-2-ylidene, a benzimidazol-2-ylidene, a mesoionic 1,2,3-triazolylidene, or an imidazol-4-ylidene ligand. Tridentate donor-functionalized N-heterocyclic carbene complexes thus fall outside the scope of the review. Applications in (asymmetric) transfer hydrogenation of ketones, aldehydes, imines, alkenes, and nitrobenzene are discussed.
Keywords: bidentate N-heterocyclic carbene; ruthenium; transfer hydrogenation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


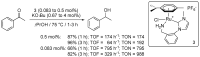
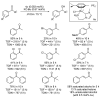
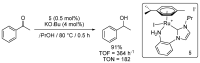

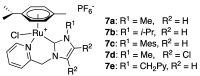





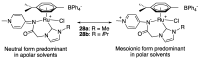






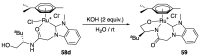
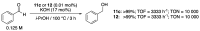


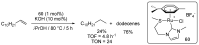

References
-
- Zassinovich G., Mestroni G., Gladiali S. Asymmetric hydrogen transfer reactions promoted by homogeneous transition metal catalysts. Chem. Rev. 1992;92:1051–1069. doi: 10.1021/cr00013a015. - DOI
-
- Noyori R., Hashiguchi S. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997;30:97–102. doi: 10.1021/ar9502341. - DOI
-
- Clapham S.E., Hadzovic A., Morris R.H. Mechanisms of the H2-hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenation of polar bonds catalyzed by ruthenium hydride complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004;248:2201–2237. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.04.007. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

