Blending Technology Based on HPLC Fingerprint and Nonlinear Programming to Control the Quality of Ginkgo Leaves
- PMID: 35897910
- PMCID: PMC9332425
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154733
Blending Technology Based on HPLC Fingerprint and Nonlinear Programming to Control the Quality of Ginkgo Leaves
Abstract
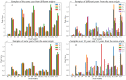
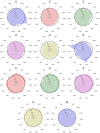
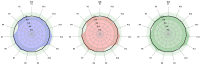
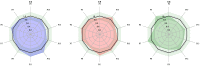
The breadth and depth of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) applications have been expanding in recent years, yet the problem of quality control has arisen in the application process. It is essential to design an algorithm to provide blending ratios that ensure a high overall product similarity to the target with controlled deviations in individual ingredient content. We developed a new blending algorithm and scheme by comparing different samples of ginkgo leaves. High-consistency samples were used to establish the blending target, and qualified samples were used for blending. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used as the sample screening method. A nonlinear programming algorithm was applied to calculate the blending ratio under different blending constraints. In one set of calculation experiments, the result was blended by the same samples under different conditions. Its relative deviation coefficients (RDCs) were controlled within ±10%. In another set of calculations, the RDCs of more component blending by different samples were controlled within ±20%. Finally, the near-critical calculation ratio was used for the actual experiments. The experimental results met the initial setting requirements. The results show that our algorithm can flexibly control the content of TCMs. The quality control of the production process of TCMs was achieved by improving the content stability of raw materials using blending. The algorithm provides a groundbreaking idea for quality control of TCMs.
Keywords: ginkgo leaves; high-performance liquid chromatography; natural herb blending; stoichiometry; traditional Chinese medicine quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Feng Y., Duez P., Hendry B. The art and science of traditional medicine part 1: TCM today—A case for integration. Science. 2014;346:1569.
-
- Ihl R., Tribanek M., Bachinskaya N., Group G.S. Efficacy and tolerability of a once daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia: Results from a randomised controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2012;45:41–46. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1291217. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

