Exploring the Interaction of G-quadruplex Binders with a (3 + 1) Hybrid G-quadruplex Forming Sequence within the PARP1 Gene Promoter Region
- PMID: 35897968
- PMCID: PMC9369712
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154792
Exploring the Interaction of G-quadruplex Binders with a (3 + 1) Hybrid G-quadruplex Forming Sequence within the PARP1 Gene Promoter Region
Abstract
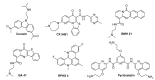
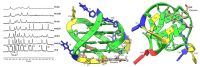
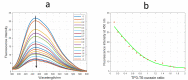
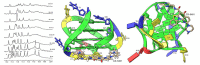
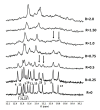
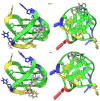
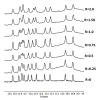
The enzyme PARP1 is an attractive target for cancer therapy, as it is involved in DNA repair processes. Several PARP1 inhibitors have been approved for clinical treatments. However, the rapid outbreak of resistance is seriously threatening the efficacy of these compounds, and alternative strategies are required to selectively regulate PARP1 activity. A noncanonical G-quadruplex-forming sequence within the PARP1 promoter was recently identified. In this study, we explore the interaction of known G-quadruplex binders with the G-quadruplex structure found in the PARP gene promoter region. The results obtained by NMR, CD, and fluorescence titration, also confirmed by molecular modeling studies, demonstrate a variety of different binding modes with small stabilization of the G-quadruplex sequence located at the PARP1 promoter. Surprisingly, only pyridostatin produces a strong stabilization of the G-quadruplex-forming sequence. This evidence makes the identification of a proper (3+1) stabilizing ligand a challenging goal for further investigation.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; NMR; PARP1 promoter; circular dichroism; fluorescence; molecular modeling; stabilizing ligand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Investigation of the Complexes Formed between PARP1 Inhibitors and PARP1 G-Quadruplex at the Gene Promoter Region.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 14;22(16):8737. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168737. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445442 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a (3+1) hybrid G-quadruplex in the PARP1 promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Feb 20;47(3):1564-1572. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1179. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30551210 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the mechanism of binding of doxorubicin and a chlorin compound with 22-mer c-Myc G quadruplex.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2023 Dec;1867(12):130482. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2023.130482. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2023. PMID: 37821013
-
Interaction of G-quadruplexes with nonintercalating duplex-DNA minor groove binding ligands.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Dec 21;22(12):2355-68. doi: 10.1021/bc200268a. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 22074555 Review.
-
DNA and RNA quadruplex-binding proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 29;15(10):17493-517. doi: 10.3390/ijms151017493. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25268620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Molecular Structure, Stability, and Biological Significance of Non-Canonical DNA Forms, with a Focus on G-Quadruplexes and i-Motifs.Molecules. 2024 Oct 2;29(19):4683. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194683. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morales J., Li L., Fattah F.J., Dong Y., Bey E.A., Patel M., Gao J., Boothman D.A. Review of Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Mechanisms of Action and Rationale for Targeting in Cancer and Other Diseases. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2014;24:15–28. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2013006875. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

