BO-ALLCNN: Bayesian-Based Optimized CNN for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Detection in Microscopic Blood Smear Images
- PMID: 35898023
- PMCID: PMC9329984
- DOI: 10.3390/s22155520
BO-ALLCNN: Bayesian-Based Optimized CNN for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Detection in Microscopic Blood Smear Images
Abstract
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a deadly cancer characterized by aberrant accumulation of immature lymphocytes in the blood or bone marrow. Effective treatment of ALL is strongly associated with the early diagnosis of the disease. Current practice for initial ALL diagnosis is performed through manual evaluation of stained blood smear microscopy images, which is a time-consuming and error-prone process. Deep learning-based human-centric biomedical diagnosis has recently emerged as a powerful tool for assisting physicians in making medical decisions. Therefore, numerous computer-aided diagnostic systems have been developed to autonomously identify ALL in blood images. In this study, a new Bayesian-based optimized convolutional neural network (CNN) is introduced for the detection of ALL in microscopic smear images. To promote classification performance, the architecture of the proposed CNN and its hyperparameters are customized to input data through the Bayesian optimization approach. The Bayesian optimization technique adopts an informed iterative procedure to search the hyperparameter space for the optimal set of network hyperparameters that minimizes an objective error function. The proposed CNN is trained and validated using a hybrid dataset which is formed by integrating two public ALL datasets. Data augmentation has been adopted to further supplement the hybrid image set to boost classification performance. The Bayesian search-derived optimal CNN model recorded an improved performance of image-based ALL classification on test set. The findings of this study reveal the superiority of the proposed Bayesian-optimized CNN over other optimized deep learning ALL classification models.
Keywords: Bayesian optimization; CNN; classification; convolutional neural network; deep learning; hyperparameter optimization; leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
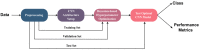



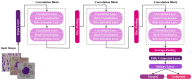

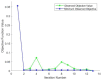

References
-
- Common Cancer Types—NCI. [(accessed on 1 July 2022)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/common-cancers.
-
- Leukemia—Cancer Stat Facts. [(accessed on 30 June 2022)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/leuks.html.
-
- Emadi A., Karp J.E. Acute Leukemia: An Illustrated Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018;6:951–952.
-
- Ghaderzadeh M., Asadi F., Hosseini A., Bashash D., Abolghasemi H., Roshanpour A. Machine Learning in Detection and Classification of Leukemia Using Smear Blood Images: A Systematic Review. Sci. Program. 2021;2021:9933481. doi: 10.1155/2021/9933481. - DOI
-
- Sajjad M., Khan S., Jan Z., Muhammad K., Moon H., Kwak J.T., Rho S., Baik S.W., Mehmood I. Leukocytes Classification and Segmentation in Microscopic Blood Smear: A Resource-Aware Healthcare Service in Smart Cities. IEEE Access. 2017;5:3475–3489. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2636218. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

