The Role of Type 2 Diabetes in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 35898377
- PMCID: PMC9308974
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26288
The Role of Type 2 Diabetes in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
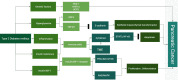
The incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its potential complications, such as cancers, are increasing worldwide at an astounding rate. There are many factors such as obesity, diabetes, alcohol consumption, and the adoption of sedentary lifestyles that are driving pancreatic cancer (PC) to become one of the leading causes of cancer mortality in the United States. PC is notorious for its generic symptoms and late-stage presentation with rapid metastasis. The connection between T2DM and the risk of PC development is multifaceted and complex. Some of the proposed theories reveal that chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and abnormalities in the insulin and insulin-like growth factor axis (IGF) contribute to the disease association between these two conditions. This literature review aims to highlight relevant studies and explore the molecular mechanisms involved in the etiology of diabetes and its impact on PC development, as well as the role of anti-diabetic agents on PC. Despite extensive studies, the exact interaction between T2DM and PC remains obscure and will need further investigation. According to current knowledge, there is a substantial link between diabetes, obesity, and dietary patterns in the development and progression of PC. Consequently, focusing our efforts on preventive measures by reducing modifiable risk factors remains the most effective strategy to reduce the risk of PC at this time. Antidiabetic drugs can have various effects on the occurrence and prognosis of PC with metformin offering a clear benefit of inhibiting PC and insulin increasing the risk of PC. The development of future novel therapies will require a deeper knowledge of the triggering mechanisms and interplay between these two disease states.
Keywords: antidiabetic agents; diabetes mellitus type 2; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; pancreatic neoplasm; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022, George et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Pancreatic cancer. Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16022. - PubMed
-
- Cancer stat facts: pancreatic cancer. [ May; 2022 ];https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html 2022
-
- Leading sites of new cancer cases and deaths-2022 estimates. [ May; 2022 ];https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-... 2022
-
- Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Key statistics for pancreatic cancer. [ May; 2022 ];https://www.cancer.org/cancer/pancreatic-cancer/about/key-statistics.html 2022
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
