Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for the Treatment of Diabetic Wound: From Basic Study to Clinical Application
- PMID: 35898452
- PMCID: PMC9309392
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.882469
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for the Treatment of Diabetic Wound: From Basic Study to Clinical Application
Abstract
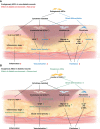
Diabetic wounds significantly affect the life quality of patients and may cause amputation and mortality if poorly managed. Recently, a wide range of cell-based methods has emerged as novel therapeutic methods in treating diabetic wounds. Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) are considered to have the potential for widespread clinical application of diabetic wounds treatment in the future. This review summarized the mechanisms of ASCs to promote diabetic wound healing, including the promotion of immunomodulation, neovascularization, and fibro synthesis. We also review the current progress and limitations of clinical studies using ASCs to intervene in diabetic wound healing. New methods of ASC delivery have been raised in recent years to provide a standardized and convenient use of ASCs.
Keywords: adipose-derived stem cells (ASC); cell therapy; diabetic ulcer; diabetic wound; diabetic wound healing.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Dong, Chang, Liang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

