Alterations of Cytokine Profiles in Patients With Recurrent Implantation Failure
- PMID: 35898466
- PMCID: PMC9309554
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.949123
Alterations of Cytokine Profiles in Patients With Recurrent Implantation Failure
Abstract
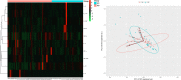
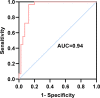
Serum cytokine profile and T helper (Th)1/Th2 cell balance are related to the success of embryo implantation, although not yet firmly linked to recurrent implantation failure (RIF), a repeated failure to achieve clinical pregnancy following multiple high-quality embryo transfer. In this prospective study, comprehensive bioinfomatic analysis and logistic regression analysis were used to compare the serum cytokine profiles of 41 RIF patients with those of 29 subjects with first-cycle successful pregnancy in the mid-luteal phase and to assess the alterations of cytokine profiles in patients with clinical pregnancy at five weeks post-transplantation. We found several elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines, decreased anti-inflammatory cytokines, and increased Th1/Th2 cytokine ratios in RIF patients compared to control subjects. Specifically, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve generated using multiple indicators provides a high predictive value for diagnosing RIF (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.94, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.87-1.00, P < 0.0001), with a sensitivity of 96.55% and a specificity of 87.50%. Meanwhile, at five weeks post-transplantation, patients in both groups diagnosed with clinical pregnancy exhibited increased levels of several cytokines compared with pre-pregnancy levels, and a gradual shift in Th1/Th2 balance toward Th2. These findings suggest that inflammatory serum cytokines and the predominance of Th1 cells likely contribute to RIF and possibly reflect the immune environment at the maternal-fetal interface, suggesting their value as outcome indicators in assisted reproductive therapy.
Keywords: Th1/Th2; cytokines; in vitro fertilization; logistic regression analysis; recurrent implantation failure.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Guo, Yang, Li, Yan, Deng, Dai and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of probiotics in restoring the Th1 to Th2 ratio in women experiencing recurrent implantation failure; a double-blind randomized clinical trial.Hum Immunol. 2025 Jan;86(1):111220. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2024.111220. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Hum Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39705908 Clinical Trial.
-
Immunosuppression with tacrolimus improved reproductive outcome of women with repeated implantation failure and elevated peripheral blood TH1/TH2 cell ratios.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2015 Apr;73(4):353-61. doi: 10.1111/aji.12338. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25394810
-
Recurrent implantation failure and inflammatory markers in serum and follicle fluid of women undergoing assisted reproduction.J Reprod Immunol. 2024 Mar;162:104209. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2024.104209. Epub 2024 Jan 30. J Reprod Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38310681
-
T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 18;11:2025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02025. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What is the impact of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in subcutaneous injection or intrauterine infusion and during both the fresh and frozen embryo transfer cycles on recurrent implantation failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis?Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Aug 13;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00810-4. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34388994 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Immunological Aspects and Treatments of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss and Recurrent Implantation Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 3;26(3):1295. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031295. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic Analysis of the Significance of the KIR2DL4 Gene in Recurrent Implantation Failure.Biochem Genet. 2025 Aug;63(4):2893-2911. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10857-8. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 38858283
-
Decidualized human decidual stromal cells inhibit chemotaxis of activated T cells: a potential mechanism of maternal-fetal immune tolerance.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 23;14:1223539. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1223539. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37680635 Free PMC article.
-
Uterine Nodal expression supports maternal immunotolerance and establishment of the FOXP3+ regulatory T cell population during the preimplantation period.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1276979. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1276979. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022561 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

