Identification of vaccine candidate against Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 using immunoinformatic approaches
- PMID: 35898574
- PMCID: PMC9315333
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-022-00128-y
Identification of vaccine candidate against Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 using immunoinformatic approaches
Abstract
Despite the availability of COVID-19 vaccines, additional more potent vaccines are still required against the emerging variations of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In the present investigation, we have identified a promising vaccine candidate against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) using immunoinformatics approaches. Various available tools like, the Immune Epitope Database server resource, and NetCTL-1.2, have been used for the identification of the promising T-cell and B-cell epitopes. The molecular docking was performed to check the interaction of TLR-3 receptors and validated 3D model of vaccine candidate. The codon optimization was done followed by cloning using SnapGene. Finally, In-silico immune simulation profile was also checked. The identified T-cell and B-cell epitopes have been selected based on their antigenicity (VaxiJen v2.0) and, allergenicity (AllerTOP v2.0). The identified epitopes with antigenic and non-allergenic properties were fused with the specific peptide linkers. In addition, the 3D model was constructed by the PHYRE2 server and validated using ProSA-web. The validated 3D model was further docked with the Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and showed good interaction with the amino acids which indicate a promising vaccine candidate against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Finally, the codon optimization, In-silico cloning and immune simulation profile was found to be satisfactory. Overall, the designed vaccine candidate has a potential against variant of SARS-Cov-2. However, further experimental studies are required to confirm.
Keywords: B-cell; Docking; Immunoinformatics; Immunology; Omicron; T-cell; Vaccine.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

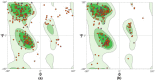
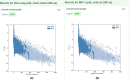
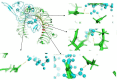


References
-
- Allergen fp v1.0 server. Available at https://ddg-pharmfac.net/AllergenFP/. Accessed 6th January 2022
-
- AllerTOP v2.0 server. Available at https://www.ddg-pharmfac.net/AllerTOP/. Accessed 15 January 2022
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

