Social Cognition in Adult ADHD: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35898990
- PMCID: PMC9311421
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.940445
Social Cognition in Adult ADHD: A Systematic Review
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Social cognition in adult ADHD: a systematic review.Front Psychol. 2024 Dec 10;15:1509848. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1509848. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39723398 Free PMC article.
Abstract
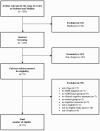
The aim of this systematic review was to collect and align the research on social cognition impairments in adults with Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In particular, we selected and analyzed papers on emotion recognition and processing, Theory of Mind (TOM), empathy, and other facets of social cognition as decision making. We identified 16 papers published between 2012 and 2022 which meet inclusion criteria. Papers search, selection, and extraction followed the PRISMA guidelines. In order to summarize data from papers, we used a narrative synthesis approach. Results show different evidence of impairment in social cognition domains in adults with ADHD. Our systematic review suggests the importance of promoting more research on this topic because it is essential to keep in mind that social cognition plays a central role in socialization and social relationships.
Keywords: adults ADHD; decision making; emotion recognition and processing; empathy; executive functions; social cognition; theory of mind.
Copyright © 2022 Morellini, Ceroni, Rossi, Zerboni, Rege-Colet, Biglia, Morese and Sacco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edn. Washington, DC: Author.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources