Heart Sparing Radiotherapy Techniques in Breast Cancer: A Focus on Deep Inspiration Breath Hold
- PMID: 35899145
- PMCID: PMC9309321
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S282799
Heart Sparing Radiotherapy Techniques in Breast Cancer: A Focus on Deep Inspiration Breath Hold
Abstract
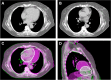
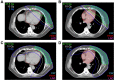
Adjuvant radiation therapy is a critical component of breast cancer management. However, when breast cancer patients receive incidental radiation to the heart, there is an increased risk of cardiac disease and mortality. This is most common for patients with left-sided breast cancers and those receiving nodal irradiation as part of treatment. The overall risk of cardiac toxicity increases 4-16% with each Gray increase in mean heart radiation dose, with data suggesting that no lower limit exists which would eliminate cardiac risk entirely. Radiation techniques have improved over time, leading to lower cardiac radiation exposure than in the past. This decline is expected to reduce the incidence of radiation-induced heart dysfunction in patients. Deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH) is one such technique that was developed to reduce the risk of cardiac death and coronary events. DIBH is a non-invasive approach that capitalizes on the natural physiology of the respiratory cycle to increase the distance between the heart and the therapeutic target throughout the course of radiation therapy. DIBH has been shown to decrease the mean incidental radiation doses to the heart and left anterior descending coronary artery by approximately 20-70%. In this review, we summarize different techniques for DIBH and discuss recent data on this technique.
Keywords: active breathing control; breast cancer; deep inspiration breath hold; heart; radiation; real-time position management.
© 2022 Stowe et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac dose-sparing effects of deep-inspiration breath-hold in left breast irradiation : Is IMRT more beneficial than VMAT?Strahlenther Onkol. 2017 Oct;193(10):800-811. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1167-0. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017. PMID: 28646251 Clinical Trial. English.
-
Dosimetric Planning Comparison for Left-Sided Breast Cancer Radiotherapy: The Clinical Feasibility of Four-Dimensional-Computed Tomography-Based Treatment Planning Optimization.Cureus. 2022 May 6;14(5):e24777. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24777. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35673303 Free PMC article.
-
Deep inspiration breath-hold radiation therapy in left-sided breast cancer patients: a single-institution retrospective dosimetric analysis of organs at risk doses.Strahlenther Onkol. 2023 Apr;199(4):379-388. doi: 10.1007/s00066-022-01998-z. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Strahlenther Onkol. 2023. PMID: 36074138 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Inspiration Breath Hold: Techniques and Advantages for Cardiac Sparing During Breast Cancer Irradiation.Front Oncol. 2018 Apr 4;8:87. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00087. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29670854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cardiac dose-sparing benefits of deep inspiration breath-hold in left breast irradiation: a systematic review.J Med Radiat Sci. 2015 Mar;62(1):66-73. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.89. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Med Radiat Sci. 2015. PMID: 26229669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond surgery: the proper role and delivery of radiation therapy in the local-regional management of BIA-ALCL.Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2024 Aug 7;11(1):2389172. doi: 10.1080/23320885.2024.2389172. eCollection 2024. Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2024. PMID: 39119029 Free PMC article.
-
Internal mammary node irradiation in early breast cancer - target coverage and implications on dose to organs at risk.Acta Oncol. 2025 Jul 30;64:989-996. doi: 10.2340/1651-226X.2025.43716. Acta Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40734573 Free PMC article.
-
Current Cardioprotective Strategies for the Prevention of Radiation-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Left-Sided Breast Cancer Patients.J Pers Med. 2023 Jun 24;13(7):1038. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071038. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37511651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of deep inspiration breath hold, surface-guided radiotherapy, and daily CBCT on the organs at risk in breast cancer radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27814. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77482-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537683 Free PMC article.
-
Automated review of patient position in DIBH breast hybrid IMRT with EPID images.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Sep;24(9):e14038. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14038. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 37449391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10 801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9804):1707–1716. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61629-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

