Functions and Interactions of Mammalian KDM5 Demethylases
- PMID: 35899196
- PMCID: PMC9309374
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.906662
Functions and Interactions of Mammalian KDM5 Demethylases
Abstract
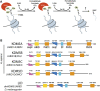
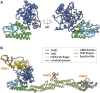
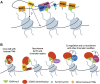
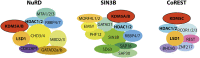
Mammalian histone demethylases of the KDM5 family are mediators of gene expression dynamics during developmental, cellular differentiation, and other nuclear processes. They belong to the large group of JmjC domain containing, 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) dependent oxygenases and target methylated lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4me1/2/3), an epigenetic mark associated with active transcription. In recent years, KDM5 demethylases have gained increasing attention due to their misregulation in many cancer entities and are intensively explored as therapeutic targets. Despite these implications, the molecular basis of KDM5 function has so far remained only poorly understood. Little is known about mechanisms of nucleosome recognition, the recruitment to genomic targets, as well as the local regulation of demethylase activity. Experimental evidence suggests close physical and functional interactions with epigenetic regulators such as histone deacetylase (HDAC) containing complexes, as well as the retinoblastoma protein (RB). To understand the regulation of KDM5 proteins in the context of chromatin, these interactions have to be taken into account. Here, we review the current state of knowledge on KDM5 function, with a particular emphasis on molecular interactions and their potential implications. We will discuss and outline open questions that need to be addressed to better understand histone demethylation and potential demethylation-independent functions of KDM5s. Addressing these questions will increase our understanding of histone demethylation and allow us to develop strategies to target individual KDM5 enzymes in specific biological and disease contexts.
Keywords: JmjC oxygenases; KDM5; epigenetics; gene regulation; histone demethylation.
Copyright © 2022 Pavlenko, Ruengeler, Engel and Poepsel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of KDM5 lysine demethylase family substrate preference and identification of novel substrates.J Biochem. 2022 Dec 27;173(1):31-42. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvac081. J Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36205465
-
The catalytic domains of all human KDM5 JmjC demethylases catalyse N-methyl arginine demethylation.FEBS Lett. 2023 Apr;597(7):933-946. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14586. Epub 2023 Feb 7. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36700827 Free PMC article.
-
The Histone Demethylase KDM5 Activates Gene Expression by Recognizing Chromatin Context through Its PHD Reader Motif.Cell Rep. 2015 Dec 15;13(10):2219-31. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26673323 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Functions of KDM5 in Cancer: Transcriptional Repressor or Activator?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;14(13):3270. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133270. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35805040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KDM5 demethylases and their role in cancer cell chemoresistance.Int J Cancer. 2019 Jan 15;144(2):221-231. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31881. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30246379 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequential deregulation of histone marks, chromatin accessibility and gene expression in response to PROTAC-induced degradation of ASH2L.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 19;13(1):22565. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49284-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38114530 Free PMC article.
-
Escape of Kdm6a from X chromosome is detrimental to ischemic brains via IRF5 signaling.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 27:rs.3.rs-4986866. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4986866/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Jan 3. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01321-1. PMID: 39399684 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Histone demethylase enzymes KDM5A and KDM5B modulate immune response by suppressing transcription of endogenous retroviral elements.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 25:2024.09.23.614494. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.23.614494. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39386707 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Versatile JMJD proteins: juggling histones and much more.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Sep;49(9):804-818. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38926050 Review.
-
To Erase or Not to Erase: Non-Canonical Catalytic Functions and Non-Catalytic Functions of Members of Histone Lysine Demethylase Families.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 24;25(13):6900. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136900. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000010 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

