Comparative global B cell receptor repertoire difference induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination via single-cell V(D)J sequencing
- PMID: 35899581
- PMCID: PMC9377262
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2105261
Comparative global B cell receptor repertoire difference induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination via single-cell V(D)J sequencing
Abstract
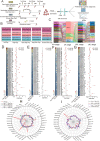
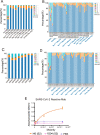
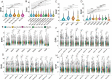
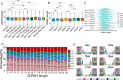
Dynamic changes of the paired heavy and light chain B cell receptor (BCR) repertoire provide an essential insight into understanding the humoral immune response post-SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. However, differences between the endogenous paired BCR repertoire kinetics in SARS-CoV-2 infection and previously recovered/naïve subjects treated with the inactivated vaccine remain largely unknown. We performed single-cell V(D)J sequencing of B cells from six healthy donors with three shots of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (BBIBP-CorV), five people who received the BBIBP-CorV vaccine after having recovered from COVID-19, five unvaccinated COVID-19 recovered patients and then integrated with public data of B cells from four SARS-CoV-2-infected subjects. We discovered that BCR variable (V) genes were more prominently used in the SARS-CoV-2 exposed groups (both in the group with active infection and in the group that had recovered) than in the vaccinated groups. The VH gene that expanded the most after SARS-CoV-2 infection was IGHV3-33, while IGHV3-23 in the vaccinated groups. SARS-CoV-2-infected group enhanced more BCR clonal expansion and somatic hypermutation than the vaccinated healthy group. A small proportion of public clonotypes were shared between the SARS-CoV-2 infected, vaccinated healthy, and recovered groups. Moreover, several public antibodies had been identified against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. We comprehensively characterize the paired heavy and light chain BCR repertoire from SARS-CoV-2 infection to vaccination, providing further guidance for the development of the next-generation precision vaccine.
Keywords: BCR repertoire; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 infection; SARS-CoV-2 vaccination; inactivated vaccine; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
