Endothelial UCP2 Is a Mechanosensitive Suppressor of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 35899624
- PMCID: PMC9390236
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321187
Endothelial UCP2 Is a Mechanosensitive Suppressor of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Inflamed endothelial cells (ECs) trigger atherogenesis, especially at arterial regions experiencing disturbed blood flow. UCP2 (Uncoupling protein 2), a key mitochondrial antioxidant protein, improves endothelium-dependent relaxation in obese mice. However, whether UCP2 can be regulated by shear flow is unknown, and the role of endothelial UCP2 in regulating inflammation and atherosclerosis remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the mechanoregulation of UCP2 expression in ECs and the effect of UCP2 on endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis.
Methods: In vitro shear stress simulation system was used to investigate the regulation of UCP2 expression by shear flow. EC-specific Ucp2 knockout mice were used to investigate the role of UCP2 in flow-associated atherosclerosis.
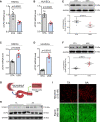
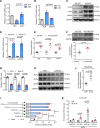
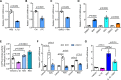
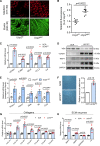
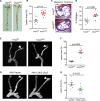
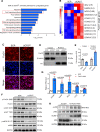
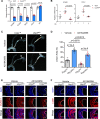
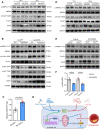
Results: Shear stress experiments showed that KLF2 (Krüppel-like factor 2) mediates fluid shear stress-dependent regulation of UCP2 expression in human aortic and human umbilical vein ECs. Unidirectional shear stress, statins, and resveratrol upregulate whereas oscillatory shear stress and proinflammatory stimuli inhibit UCP2 expression through altered KLF2 expression. KLF2 directly binds to UCP2 promoter to upregulate its transcription in human umbilical vein ECs. UCP2 knockdown induced expression of genes involved in proinflammatory and profibrotic signaling, resulting in a proatherogenic endothelial phenotype. EC-specific Ucp2 deletion promotes atherogenesis and collagen production. Additionally, we found endothelial Ucp2 deficiency aggravates whereas adeno-associated virus-mediated EC-Ucp2 overexpression inhibits carotid atherosclerotic plaque formation in disturbed flow-enhanced atherosclerosis mouse model. RNA-sequencing analysis revealed FoxO1 (forkhead box protein O1) as the major proinflammatory transcriptional regulator activated by UCP2 knockdown, and FoxO1 inhibition reduced vascular inflammation and disturbed flow-enhanced atherosclerosis. We showed further that UCP2 level is critical for phosphorylation of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), which is required for UCP2-induced inhibition of FoxO1.
Conclusions: Altogether, our studies uncover that UCP2 is novel mechanosensitive gene under the control of fluid shear stress and KLF2 in ECs. UCP2 expression is critical for endothelial proinflammatory response and atherogenesis. Therapeutic strategies enhancing UCP2 level may have therapeutic potential against atherosclerosis.
Keywords: antioxidants; atherosclerosis; endothelial cell; inflammation; resveratrol.
Figures
References
-
- Ku KH, Subramaniam N, Marsden PA. Epigenetic determinants of flow-mediated vascular endothelial gene expression. Hypertension. 2019;74:467–476. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13342 - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Luo JY, Li B, Tian XY, Chen LJ, Huang Y, Liu J, Deng D, Lau CW, Wan S, et al. . Integrin-YAP/TAZ-JNK cascade mediates atheroprotective effect of unidirectional shear flow. Nature. 2016;540:579–582. doi: 10.1038/nature20602 - PubMed
-
- Weber C, Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. 2011;17:1410–1422. doi: 10.1038/nm.2538 - PubMed
-
- VanderLaan PA, Reardon CA, Getz GS. Site specificity of atherosclerosis: site-selective responses to atherosclerotic modulators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:12–22. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000105054.43931.f0 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

