A Randomized Thorough QT Study of Apomorphine Sublingual Film in Patients With Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 35899977
- PMCID: PMC9541463
- DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.1147
A Randomized Thorough QT Study of Apomorphine Sublingual Film in Patients With Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
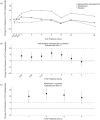
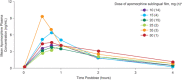
A randomized thorough QT study was conducted to assess the effects of apomorphine sublingual film (SL-APO) on corrected QT interval (QTc) and other cardiac conduction parameters in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and "OFF" episodes. Patients were titrated to an SL-APO dose that resulted in FULL "ON," followed by up to two additional doses (maximum 60 mg), then randomized at the highest tolerated dose to a treatment sequence of SL-APO, placebo, and moxifloxacin (400 mg, positive control) in a three-way crossover design. Changes from baseline in time-matched, placebo-adjusted Fridericia-corrected QTc interval (ΔΔQTcF) and Bazett-corrected QTc interval (ΔΔQTcB) were analyzed from postdose electrocardiograms. Forty patients were randomized and received single doses of study treatments. Upper limits of 90% confidence intervals (CIs) for ΔΔQTcF of SL-APO were below the 10-millisecond regulatory threshold at all prespecified timepoints, demonstrating no clinically significant effect on QTcF. Lower limits of 90% CIs for ΔΔQTcF of moxifloxacin exceeded the 5-millisecond regulatory threshold at all timepoints up to 3 hours, confirming assay sensitivity. SL-APO had no clinically meaningful effects on QTcB, PR/QRS intervals, heart rate, or electrocardiogram-derived morphology (EudraCT identifier: 2016-001762-29; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03187301).
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; QT interval; apomorphine sublingual film; pharmacokinetics; “OFF” episodes.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
F.S. and E.L.P. received research/grant support from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. for participation in this study. M.F.D.P. reports no conflicts of interest. K.S. and F.A. are full‐time employees of Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. and may hold stock/stock options in the company. R.K. is an employee of eResearch Technology Inc. (ERT) and performs consulting services for various pharmaceutical companies, including Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc., for which ERT receives payment. C.W.O. owns shares in Clintrex Research Corporation, which has received fees from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. D.B. and B.N. were employees of Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. at the time the study was conducted.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong MJ, Okun MS. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA. 2020;323(6):548‐560. - PubMed
-
- Olanow CW, Stocchi F. Levodopa: a new look at an old friend. Mov Disord. 2018;33(6):859‐866. - PubMed
-
- Olanow CW, Stern MB, Sethi K. The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2009;72(21 Suppl 4):S1‐S136. - PubMed
-
- Chou KL, Stacy M, Simuni T, et al. The spectrum of “OFF” in Parkinson's disease: what have we learned over 40 years? Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018;51:9‐16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

