Treatment of centered developmental dysplasia of the hip under the age of 1 year: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline - Part 1
- PMID: 35900213
- PMCID: PMC9297049
- DOI: 10.1530/EOR-21-0125
Treatment of centered developmental dysplasia of the hip under the age of 1 year: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline - Part 1
Abstract
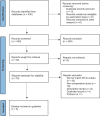
Despite the high incidence of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), treatment is very diverse. Therefore, the Dutch Orthopedic Society developed a clinical practice guideline with recommendations for optimal and uniform treatment of DDH. This article summarizes the guideline on centered DDH (i.e. Graf types 2A-C). The guideline development followed the criteria of Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II. A systematic literature review was performed to identify randomized controlled trials and comparative cohort studies including children <1 year with centered DDH. Articles were included that compared (1) treatment with observation, (2) different abduction devices, (3) follow-up frequencies, and (4) discontinuation methods. Recommendations were based on Grading Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation, which included the literature, clinical experience and consensus, patient and parent comfort, and costs. Out of 430 potentially relevant articles, 5 comparative studies were included. Final guideline recommendations were (1) initially observe 3-month-old patients with centered DDH, start abduction treatment if the hip does not normalize after 6-12 weeks; (2) prescribe a Pavlik harness to children <6 months with persisting DDH on repeated ultrasonography, consider alternative abduction devices for children >6 months; (3) assess patients every 6 weeks; and (4) discontinue the abduction device when the hip has normalized or when the child is 12 months. This paper presents a summary of part 1 of the first evidence-based guideline for treatment of centered DDH in children <1 year. Part 2 presents the guideline on decentered DDH in a separate article.
Keywords: DDH; abduction treatment; guideline.
Figures
References
-
- de Witte PB van Bergen CJA de Geest BL Willeboordse F van Linge JH den Hortog YM Foreman-van Dongelen MMHP Pereboom RM Robben SGF Burger BJ Adhiambo Witlox M & Witbreuk MMEH.. Treatment of decentered developmental dysplasia of the hip under the age of 1 year: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline - Part 2. EFORT Open Reviews. In press. (10.1530/EOR-21-0126) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials