Aromatase inhibition increases blood pressure and markers of renal injury in female rats
- PMID: 35900340
- PMCID: PMC9423724
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00055.2022
Aromatase inhibition increases blood pressure and markers of renal injury in female rats
Abstract
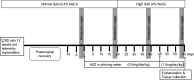
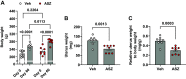
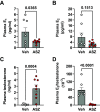
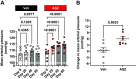
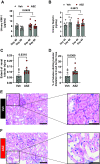
Aromatase is a monooxygenase that catalyzes the rate-limiting step of estrogen biosynthesis from androgens. Aromatase inhibitors are widely used for the treatment of patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. However, the effects of aromatase inhibitors on cardiovascular and renal health in females are understudied. Given that estrogen is protective against cardiovascular and kidney diseases, we hypothesized that aromatase inhibition elevates blood pressure and induces kidney injury in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Twelve-week-old female rats were implanted with radiotelemetry transmitters to continuously monitor blood pressure. After baseline blood pressure recording, rats were randomly assigned to treatment with the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole (ASZ) or vehicle (Veh) in drinking water. Twenty days after treatment initiation, rats were shifted from a normal-salt (NS) diet to a high-salt (HS) diet for an additional 40 days. Rats were euthanized 60 days after treatment initiation. Body weight increased in both groups over the study period, but the increase was greater in the ASZ-treated group than in the Veh-treated group. Mean arterial pressure increased in ASZ-treated rats during the NS and HS diet phases but remained unchanged in Veh-treated rats. In addition, urinary excretion of albumin and kidney injury marker-1 and plasma urea were increased in response to aromatase inhibition. Furthermore, histological assessment revealed that ASZ treatment increased morphological evidence of renal tubular injury and proximal tubular brush border loss. In conclusion, chronic aromatase inhibition in vivo with ASZ increases blood pressure and markers of renal proximal tubular injury in female Sprague-Dawley rats, suggesting an important role for aromatization in the maintenance cardiovascular and renal health in females.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Aromatase enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step in estrogen biosynthesis. Aromatase inhibitors are clinically used for the treatment of patients with breast cancer; however, the impact of inhibiting aromatization on blood pressure and renal function is incompletely understood. The present findings demonstrate that systemic anastrozole treatment increases blood pressure and renal tubular injury markers in female rats fed a high-salt diet, suggesting an important role for aromatization in preserving cardiovascular and renal health in females.
Keywords: anastrozole; dietary sodium; estrogen; hypertension; proximal tubule.
Conflict of interest statement
E.Y.G. is also affiliated with the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Alexandria University, Egypt. None of the other authors has any conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

