Now you see it, now you don't: Relevance of threat enhances social anxiety-linked attentional bias to angry faces, but relevance of neutral information attenuates it
- PMID: 35901035
- PMCID: PMC9333259
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271752
Now you see it, now you don't: Relevance of threat enhances social anxiety-linked attentional bias to angry faces, but relevance of neutral information attenuates it
Abstract
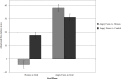
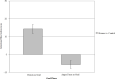
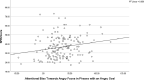
Temporary goals modulate attention to threat. We examined whether attentional bias to angry faces differs depending on whether a temporary background goal is neutral, or threat related, whilst also measuring social anxiety. Participants performed a dot probe task combined with a separate task that induced a temporary goal. Depending on the phase in this goal task, the goal made angry faces or neutral stimuli (i.e., houses) relevant. The dot probe task measured attention to combinations of angry faces, neutral but goal-relevant stimuli (i.e., houses), and neutral control stimuli. Attention was allocated to angry faces when an angry goal was active. This was more pronounced for people scoring high on social phobia. The neutral goal attenuated attention to angry faces and effects of social phobia were no longer apparent. These findings suggest that individual differences in social anxiety interact with current and temporary goals to affect attentional processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Cunningham WA, Brosch T. Motivational salience: Amygdala tuning from traits, needs, values, and goals. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2012;21:54–9. Available from: 10.1177/0963721411430832 - DOI
-
- Vuilleumier P, Huang Y-M. Emotional attention: Uncovering the mechanisms of affective biases in perception. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2009;18:148–52. Available from: 10.1111/j.1467-8721.2009.01626.x - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

