Investigating VEGF. miR-145-3p, and miR-101-3p Expression in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 35901327
- PMCID: PMC9727337
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.7.2233
Investigating VEGF. miR-145-3p, and miR-101-3p Expression in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is the second most common type of primary liver cancer. Several factors, such as epigenetic changes in promoter genes, gene expression, and microRNAs (miR), can contribute to genomic instability in cancer. This study aimed at evaluating the expression of VEGF, miRs 145-3p, and 101-3p in patients with CCA and their potential as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of CCA.
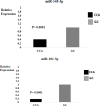
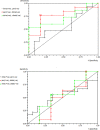
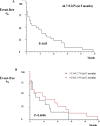
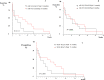
Material and methods: Sixty two patients were studied. Out of these 62 patients, 41 cases had confirm CCA and 21 cases had hepatopathies complications. The RNA was extracted from a paraffined tissue block, and then the synthesis of cDNA was performed. The analysis of the expression of VEGF, miR-145-3p, and miR-101-3p was carried out by polymerase chain reaction in real time. Results: The findings revealed that miRs 145-3p and 101-3p were under expressed in the case group compared to the control group (0.46; 0.17; P = 0.0001, respectively). VEGF was overexpressed in the case group compared to the control group (11.8; P = 0.0001). An increase in miR-145-3p expression level was observed in patients with perihilar CCA compared to those with distal CCA (0.51 ± 0.41; 0.17 ± 0.13; P = 0.0698). Survival rate analysis showed that 41.9% of patients with intrahepatic CCA and 31.5% of patients with extrahepatic CCA were free from death within 11 months, leading to a significant difference (P> 0.05).
Conclusion: The underexpression of miRNAs, tumor suppressors, the overexpression of VEGF, smoking, and aging were associated with CCA based on our findings. It seems that the reduced expression of the studies miRNAs and increased expression of VEGF can contribute to a decrease in survival rate of patients with tumor in their intrahepatic bile ducts.
Keywords: Bile Duct Diseases; Gene expression; MicroRNAs; Molecular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-551b-3p inhibits tumour growth of human cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Cyclin D1.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Aug;23(8):4945-4954. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14312. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31199052 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA myocardial infarction associated transcript promotes the proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma cells by targeting miR-551b-3p/CCND1 axis.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020 Jun;47(6):1067-1075. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13283. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32064660
-
Micro-RNA-130a-3p Regulates Gemcitabine Resistance via PPARG in Cholangiocarcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2017 Aug;24(8):2344-2352. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5871-x. Epub 2017 May 30. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28560603
-
The Role of microRNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 16;22(14):7627. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147627. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs in cholangiocarcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2023 Jan 28;553:215980. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215980. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36336149 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging assessment of residual tumor angiogenesis after insufficient microwave ablation and donafenib adjuvant therapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 24;14(1):4557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55416-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38402352 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways in liver cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy.Mol Biomed. 2024 May 31;5(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00184-0. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38816668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsa_circ_0001859 promotes NSCLC progression through the miRNA-101-3p/MMP1 axis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 1;15:1568367. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1568367. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40666104 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-101: An Important Regulator of Gene Expression and Tumor Ecosystem.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;14(23):5861. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235861. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of angiogenesis in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using MRI-based machine learning.Front Oncol. 2023 May 18;13:1048311. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1048311. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37274267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G, et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA) Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:261–80. - PubMed
-
- Brito AF, Abrantes AM, Encarnação JC, Tralhão JG, Botelho MF. Cholangiocarcinoma: From molecular biology to treatment. Med Oncol. 2015;32:245. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

