MDM2 is a Potential Target Gene of Glycyrrhizic Acid for Circumventing Breast Cancer Resistance to Tamoxifen: Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 35901340
- PMCID: PMC9727350
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.7.2341
MDM2 is a Potential Target Gene of Glycyrrhizic Acid for Circumventing Breast Cancer Resistance to Tamoxifen: Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
Background: Tamoxifen is the drug of choice for treating breast cancer, particularly the estrogen receptor-positive luminal A subtype. However, the increased occurrence of Tamoxifen resistance highlights the need to develop an agent to enhance the effectiveness of this drug.
Objective: Although glycyrrhizic acid (GA) is known to exhibit cytotoxic effects on Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 cells, the specific gene targets and pathways it employs to overcome Tamoxifen resistance are incompletely understood. Therefore, the goal of the present research is to discover the potential targets and pathways of GA by using a bioinformatics approach.
Methods: Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in the Gene Expression Omnibus NCBI database using microarray data from GSE67916 and GSE85871. Further analyses were performed on these DEGs by using DAVID v6.8, STRING-DB v11.0, and Cytoscape v3.8.0. Analysis of gene alterations was performed using cBioPortal for target validation, and the relevant interaction process was examined via the molecular docking method.
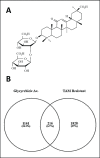
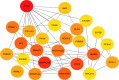
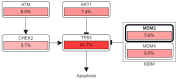
Results: Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses identified the PI3K-AKT signaling as the potential target mechanism. Construction of the protein-protein interaction network and analysis of hub genes identified the top 25 hub genes. Genetic alterations were observed in six potential target genes, such as CDK2, MDM2, NF1, SMAD3, PTPN11, and CALM1. Molecular docking analysis demonstrated that the docking score of GA is lower than that of the native ligand of p53. More importantly, 3n the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway is a potential target for overcoming Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer.
Conclusion: MDM2 may be a potential gene target of GA and the PI3K-AKT signaling may be a prospective mechanism for overcoming Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Additional research is required to validate the findings of this study.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Glycyrrhizic Acid; breast cancer; tamoxifen resistance.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In Silico Analysis Reveals MDM2 as a Potential Target of Ursolic Acid for Overcoming Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Aug 1;26(8):2899-2907. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.8.2899. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40849706
-
Genomic Understanding Reveals the Important Role of FGFR2 as Paeoniflorin Target for Circumventing Breast Cancer Resistance to Tamoxifen.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Dec 1;22(12):3949-3958. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.12.3949. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34967576 Free PMC article.
-
Functional network analysis of p85 and PI3K as potential gene targets and mechanism of oleanolic acid in overcoming breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 28;20(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s43141-022-00341-4. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35482141 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals Potential Target Genes and TNFα Signaling Inhibition by Brazilin in Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Sep 1;21(9):2751-2762. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.9.2751. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32986377 Free PMC article.
-
Common gene signatures and key pathways in hypopharyngeal and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatic analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 16;99(42):e22434. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022434. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33080677 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Oxo berberine Compound in Arcangelisia flava Root Extract for Breast Cancer Treatment: Metabolite Profiling, Pharmacological Network Analysis, and In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Apr 1;26(4):1313-1328. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.4.1313. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40302084 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Screening Using a Combination of Ligand-Based Machine Learning and Molecular Docking Methods for the Repurposing of Antivirals Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):47-65. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00484-w. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Daru. 2024. PMID: 37907683 Free PMC article.
-
Glycyrrhizin enhances the antitumor activity of cisplatin in non‑small cell lung cancer cells by influencing DNA damage and apoptosis.Oncol Lett. 2025 Mar 4;29(4):207. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14954. eCollection 2025 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40070780 Free PMC article.
-
Phytometabolites as modulators of breast cancer: a comprehensive review of mechanistic insights.Med Oncol. 2024 Jan 3;41(2):45. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02269-2. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38172452 Review.
References
-
- Comşa Ş, Cîmpean AM, Raica M. The story of MCF-7 breast cancer cell line: 40 years of experience in research. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:3147–54. - PubMed
-
- Dey R, Nandi S, Samadder A. Pelargonidin mediated selective activation of p53 and parp proteins in preventing food additive induced genotoxicity: an in vivo coupled in silico molecular docking study. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;156:105586. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

