Longitudinal Effects of Breast Cancer Treatment on Neural Correlates of Attention
- PMID: 35901461
- PMCID: PMC9868529
- DOI: 10.1093/arclin/acac051
Longitudinal Effects of Breast Cancer Treatment on Neural Correlates of Attention
Abstract
Objective: Cognitive dysfunction has been observed consistently in a subset of breast cancer survivors. Yet, the precise physiological and processing origins of dysfunction remain unknown. The current study examined the utility of methods and procedures based on cognitive neuroscience to study cognitive change associated with cancer and cancer treatment.
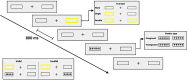
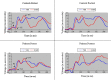
Methods: We used electroencephalogram and behavioral measures in a longitudinal design to investigate pre- versus post-treatment effects on attention performance in breast cancer patients (n = 15) compared with healthy controls (n = 24), as participants completed the revised Attention Network Test, a cognitive measure of alerting, orienting, and inhibitory control of attention.
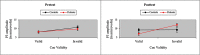
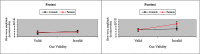
Results: We found no group differences in behavioral performance from pretest to posttest, but significant event-related potential effects of cancer treatment in processing cue validity: After treatment, patients revealed decreased N1 amplitude and increased P3 amplitude, suggesting a suppressed early (N1) response and an exaggerated late (P3) response to invalid cues.
Conclusions: The results suggest that treatment-related attentional disruption begins in early sensory/perceptual processing and extends to compensatory top-down executive processes.
Keywords: Attention; Breast cancer; EEG; Executive functioning; Longitudinal.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

