A systematic review of analytical methods used in genetic association analysis of the X-chromosome
- PMID: 35901513
- PMCID: PMC9764208
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbac287
A systematic review of analytical methods used in genetic association analysis of the X-chromosome
Abstract
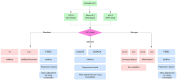
Genetic association studies have been very successful at elucidating the genetic background of many complex diseases/traits. However, the X-chromosome is often neglected in these studies because of technical difficulties and the fact that most tools only utilize genetic data from autosomes. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of different practical approaches that are followed to incorporate the X-chromosome in association analysis, such as Genome-Wide Association Studies and Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Analysis. In general, the choice of which test statistics is most appropriate will depend on three main criteria: (1) the underlying X-inactivation model, (2) if Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium holds and sex-specific allele frequencies are expected and (3) whether adjustment for confounding variables is required. All in all, it is recommended that a combination of different association tests should be used for the analysis of X-chromosome.
Keywords: GWAS; X-chromosome; X-inactivation; association analysis; eQTL; linear regression.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statistics for X-chromosome associations.Genet Epidemiol. 2018 Sep;42(6):539-550. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22132. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Genet Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29900581 Free PMC article.
-
XWAS: A Software Toolset for Genetic Data Analysis and Association Studies of the X Chromosome.J Hered. 2015 Sep-Oct;106(5):666-71. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esv059. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Hered. 2015. PMID: 26268243 Free PMC article.
-
Testing for association on the X chromosome.Biostatistics. 2008 Oct;9(4):593-600. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxn007. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Biostatistics. 2008. PMID: 18441336 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Information Improves Predictive Modeling of Disease Relevance of Non-Coding Genetic Variation.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 16;10(10):e0140758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140758. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26474488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Underlying genetic architecture of resistance to mastitis in dairy cattle: A systematic review and gene prioritization analysis of genome-wide association studies.J Dairy Sci. 2023 Jan;106(1):323-351. doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-21923. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Dairy Sci. 2023. PMID: 36333139
Cited by
-
An eQTL-based Approach Reveals Candidate Regulators of LINE-1 RNA Levels in Lymphoblastoid Cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:2023.08.15.553416. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.15.553416. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Genet. 2024 Jun 7;20(6):e1011311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011311. PMID: 37645920 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
New horizons of human genetics in digestive diseases.eGastroenterology. 2023 Nov 9;1(2):e100029. doi: 10.1136/egastro-2023-100029. eCollection 2023 Sep. eGastroenterology. 2023. PMID: 39943996 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic immune regulation and sex disparities.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Dec;21(12):869-884. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00974-5. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39237606 Review.
-
OR11H1 Missense Variant Confers the Susceptibility to Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease by Mediating Gadd45g Expression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Mar;11(11):e2306563. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306563. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38168905 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-ancestry GWAS reveals loci linked to human variation in LINE-1- and Alu-insertion numbers.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2024.09.10.612283. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.10.612283. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Transl Med Aging. 2025;9:25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tma.2025.02.001. PMID: 39314493 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.

