Clinical Outcomes After Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunting in Patients With Classic vs. Complex NPH
- PMID: 35903111
- PMCID: PMC9315242
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.868000
Clinical Outcomes After Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunting in Patients With Classic vs. Complex NPH
Abstract
Objective: Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a neurological condition characterized by a clinical triad of gait disturbance, cognitive impairment, and urinary incontinence in conjunction with ventriculomegaly. Other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and vascular dementia share some overlapping clinical features. However, there is evidence that patients with comorbid NPH and Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease may still exhibit good clinical response after CSF diversion. This study aims to evaluate clinical responses after ventriculo-peritoneal shunt (VPS) in a cohort of patients with coexisting NPH and neurodegenerative disease.
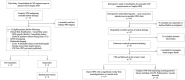
Methods: The study has two components; (i) a pilot study was performed that specifically focused upon patients with Complex NPH and following the inclusion of the Complex NPH subtype into consideration for the clinical NPH programme, (ii) a retrospective snapshot study was performed to confirm and characterize differences between Classic and Complex NPH patients being seen consecutively over the course of 1 year within a working subspecialist NPH clinic. We studied the characteristics of patients with Complex NPH, utilizing clinical risk stratification and multimodal biomarkers.
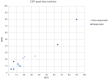
Results: There was no significant difference between responders and non-responders to CSF diversion on comorbidity scales. After VPS insertion, significantly more Classic NPH patients had improved cognition compared to Complex NPH patients (p = 0.005). Improvement in gait and urinary symptoms did not differ between the groups. 26% of the Classic NPH group showed global improvement of the triad, and 42% improved in two domains. Although only 8% showed global improvement of the triad, all Complex NPH patients improved in gait.
Conclusions: Our study has demonstrated that the presence of neurodegenerative disorders co-existing with NPH should not be the sole barrier to the consideration of high-volume tap test or lumbar drainage via a specialist NPH programme. Further characterization of distinct cohorts of NPH with differing degrees of CSF responsiveness due to overlay from neurodegenerative or comorbidity risk burden may aid toward more precise prognostication and treatment strategies. We propose a simplistic conceptual framework to describe NPH by its Classic vs. Complex subtypes to promote the clinical paradigm shift toward subspecialist geriatric neurosurgery by addressing needs for rapid screening tools at the clinical-research interface.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH); Parkinson's disease; dementia; neurodegenerative disease; ventriculo-peritoneal shunt (VPS).
Copyright © 2022 Goh, Lock, Tan, Tan, Liang, Pillay, Kumar, Ahmad-Annuar, Narayanan, Kwok, Tan, Ng, Tan, Czosnyka, Czosnyka, Pickard and Keong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lobo Antunes J, Fahn S, Cote L. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm Suppl. (1983) 19:225–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

