Influence of Fat-Soluble Vitamin Intramuscular Supplementation on Kinematic and Morphometric Sperm Parameters of Boar Ejaculates
- PMID: 35903145
- PMCID: PMC9315373
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.908763
Influence of Fat-Soluble Vitamin Intramuscular Supplementation on Kinematic and Morphometric Sperm Parameters of Boar Ejaculates
Abstract
Ejaculate quality can be regarded as multifactorial, with nutrition being a factor that could directly influence sperm parameters. The present study aimed to evaluate seminal quality associated with seasonal fat-soluble vitamin supplementation of boars. Seven sexually mature boars were randomly allotted to one of the three groups, and fed one of the three supplementary diets for 32 weeks: (1) control treatment (COD), without supplementation of fat-soluble vitamins, (2) treatment containing 100% fat-soluble vitamin supplementation administered intramuscularly, which was based on fat soluble vitamin supplementation (A, D3, E) (FVD1), and (3) treatment containing 50% of fat-soluble vitamin supplementation (FVD ). Semen was collected at 7-day intervals. Semen samples were analyzed to assess several sperm parameters using the Computer-Assisted Semen Analysis (CASA) ISAS®v1 system. Results showed that groups receiving FVD1 and FVD supplementation had an increased semen volume. The percentages of motile and progressively motile sperm were increased by FVD1 treatment. A statistically significant interaction between treatment and season was found in the percentage of motility and progressive motility (p < 0.05). Sperm concentrations showed significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatments. Velocity variables (VSL, VCL, and VAP) were higher (p < 0.05) in boars that received fat-soluble vitamin supplementation in comparison to controls receiving no supplementation. The FVD1 treatment presented spermatozoa with greater head size and more elongated heads (p < 0.05). Overall, the utilization of dietary fat-soluble vitamin supplementation significantly improved the semen quality of boar ejaculates. This highlights the importance of fat-soluble vitamin supplementation in sexually active boars.
Keywords: CASA; fat-soluble vitamin; motility; nutrition; spermatozoa.
Copyright © 2022 Calderón-Calderón, Sevilla, Roldan, Barquero and Valverde.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
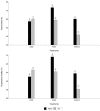
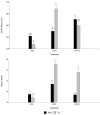
References
-
- De Ambrogi M, Ballester J, Saravia F, Caballero I, Johannisson A, Wallgren M, et al. Effect of storage in short- and long-term commercial semen extenders on the motility, plasma membrane and chromatin integrity of boar spermatozoa. Int J Androl. (2006) 29:543–52. 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2006.00694.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- González D, Quintero-Moreno A, Garde JJ, Esteso M, Fernández-Santos M, Rubio-Guillén J, et al. Caracterización morfométrica de la cabeza del espermatozoide porcino mediante análisis computarizado (resultados preliminares). Rev Cient Fac Ciencias Vet Univ del Zulia. (2008) 18:570–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

