Unraveling the Mechanism of Purple Leaf Formation in Brassica napus by Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analyses
- PMID: 35903234
- PMCID: PMC9315442
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.945553
Unraveling the Mechanism of Purple Leaf Formation in Brassica napus by Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analyses
Abstract
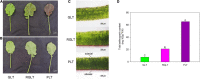
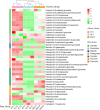
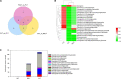
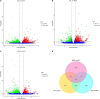
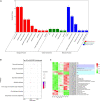
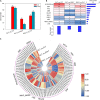
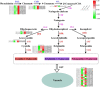
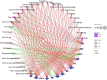
Brassica napus as both oilseed and vegetable, is widely cultivated in China. The purple leaf of B. napus is rich in anthocyanins and can provide valuable nutrients. Although several high-anthocyanin cultivars have been reported, the molecular mechanism underlying anthocyanin biosynthesis in B. napus remains lesser-known. Therefore, in this study, we conducted integrative metabolome and transcriptome analyses in three B. napus cultivars with different leaf colors. Overall, 39 flavonoids were identified (including 35 anthocyanins), and 22 anthocyanins were differentially accumulated in the leaves, contributing to the different leaf colors. Cyanidin-3,5,3'-O-triglucoside was confirmed as the main contributor of the purple leaf phenotype. Meanwhile, other anthocyanins may play important roles in deepening the color of B. napus leaves. A total of 5,069 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 32 overlapping DEGs were identified by RNA-sequencing; hence, the correlation between anthocyanin content and DEG expression levels was explored. Two structural genes (DFR and ANS), three GSTs (homologous to TT19), and 68 differentially expressed transcription factors (TFs), especially MYB-related TFs and WRKY44, were identified in three B. napus varieties characterized by different leaf color, thereby indicating that these genes may contribute to anthocyanin biosynthesis, transport, or accumulation in B. napus leaves. The findings of study provide important insights that may contribute to gaining a better understanding of the transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin metabolism in B. napus.
Keywords: Brassica napus; anthocyanin; metabolome; purple leaves; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Du, Zhang, Feng, Liu, Yang and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The introgression of BjMYB113 from Brassica juncea leads to purple leaf trait in Brassica napus.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Aug 2;24(1):735. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05418-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39090544 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal the role of BoGSTF12 in anthocyanin accumulation in Chinese kale (Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra).BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Apr 25;24(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05016-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38664614 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Identification and Comparative Expression Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthetic Genes in Brassica napus.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 18;12:764835. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.764835. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34868247 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Revealed DEGs Involved in the Purple Leaf Formation in Brassica juncea.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 24;11:322. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00322. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32391051 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress and applications of colorful Brassica crops.Planta. 2023 Jul 18;258(2):45. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04205-0. Planta. 2023. PMID: 37462779 Review.
Cited by
-
An R3-MYB repressor, BnCPC forms a feedback regulation with MBW complex to modulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in Brassica napus.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2022 Nov 29;15(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13068-022-02227-6. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2022. PMID: 36447291 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals biosynthesis genes and transcription factors related to leaf anthocyanin biosynthesis in Aglaonema commutatum.BMC Genomics. 2023 Jan 17;24(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-09107-1. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36650457 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of the purple leaf sheath in barley (Hordeum vulgare).Plant Genome. 2025 Jun;18(2):e70034. doi: 10.1002/tpg2.70034. Plant Genome. 2025. PMID: 40275436 Free PMC article.
-
The Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Regulation in Brassica napus: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 26;24(1):357. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010357. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome and metabolome analysis reveals the effect of flavonoids on flower color variation in Dendrobium nobile Lindl.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 23;14:1220507. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1220507. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37680360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asem I. D., Imotomba R. K., Mazumder P. B., Laishram J. M. (2015). Anthocyanin content in the black scented rice (Chakhao): its impact on human health and plant defense. Symbiosis 66 47–54. 10.1007/s13199-015-0329-z - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

