In Vivo Functional Assessment of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporters (SGLTs) Using [18F]Me4FDG PET in Rats
- PMID: 35903251
- PMCID: PMC9281422
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4635171
In Vivo Functional Assessment of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporters (SGLTs) Using [18F]Me4FDG PET in Rats
Abstract
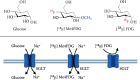
Background: Mediating glucose absorption in the small intestine and renal clearance, sodium glucose cotransporters (SGLTs) have emerged as an attractive therapeutic target in diabetic patients. A substantial fraction of patients, however, only achieve inadequate glycemic control. Thus, we aimed to assess the potential of the SGLT-targeting PET radiotracer alpha-methyl-4-deoxy-4-[18F]fluoro-D-glucopyranoside ([18F]Me4FDG) as a noninvasive intestinal and renal biomarker of SGLT-mediated glucose transport.
Methods: We investigated healthy rats using a dedicated small animal PET system. Dynamic imaging was conducted after administration of the reference radiotracer 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose ([18F]FDG), or the SGLT-targeting agent, [18F]Me4FDG either directly into the digestive tract (for assessing intestinal absorption) or via the tail vein (for evaluating kidney excretion). To confirm the specificity of [18F]Me4FDG and responsiveness to treatment, a subset of animals was also pretreated with the SGLT inhibitor phlorizin. In this regard, an intraintestinal route of administration was used to assess tracer absorption in the digestive tract, while for renal assessment, phlorizin was injected intravenously (IV).
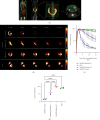
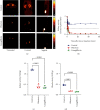
Results: Serving as reference, intestinal administration of [18F]FDG led to slow absorption with retention of 89.2 ± 3.5% of administered radioactivity at 15 min. [18F]Me4FDG, however, was rapidly absorbed into the blood and cleared from the intestine within 15 min, leading to markedly lower tracer retention of 18.5 ± 1.2% (P < 0.0001). Intraintestinal phlorizin led to marked increase of [18F]Me4FDG uptake (15 min, 99.9 ± 4.7%; P < 0.0001 vs. untreated controls), supporting the notion that this PET agent can measure adequate SGLT inhibition in the digestive tract. In the kidneys, radiotracer was also sensitive to SGLT inhibition. After IV injection, [18F]Me4FDG reabsorption in the renal cortex was significantly suppressed by phlorizin when compared to untreated animals (%ID/g at 60 min, 0.42 ± 0.10 vs. untreated controls, 1.20 ± 0.03; P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: As a noninvasive read-out of the concurrent SGLT expression in both the digestive tract and the renal cortex, [18F]Me4FDG PET may serve as a surrogate marker for treatment response to SGLT inhibition. As such, [18F]Me4FDG may enable improvement in glycemic control in diabetes by PET-based monitoring strategies.
Copyright © 2022 Yohji Matsusaka et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest as well as consent for scientific analysis and publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo assessment of safety, biodistribution, and radiation dosimetry of the [18F]Me4FDG PET-radiotracer in adults.EJNMMI Res. 2024 May 15;14(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01098-2. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 38750398 Free PMC article.
-
PET imaging of sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs): Unveiling metabolic dynamics in diabetes and oncology.Mol Metab. 2024 Dec;90:102055. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.102055. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39454827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional expression of SGLTs in rat brain.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):C1277-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00296.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20826762 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the physiological roles of SGLTs and GLUTs using positron emission tomography in mice.J Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;594(15):4425-38. doi: 10.1113/JP271904. Epub 2016 May 10. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27018980 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 and cancer.Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1407-1414. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02448-4. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Pflugers Arch. 2020. PMID: 32820343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical Evaluation of Novel SGLT2-Targeted Near-Infrared Optical Imaging Agent for Early-Stage Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma.Mol Imaging Biol. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.1007/s11307-025-02029-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Imaging Biol. 2025. PMID: 40659959
-
Molecular imaging along the heart-kidney axis.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 21;14(18):7111-7121. doi: 10.7150/thno.102552. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39629123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo assessment of safety, biodistribution, and radiation dosimetry of the [18F]Me4FDG PET-radiotracer in adults.EJNMMI Res. 2024 May 15;14(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01098-2. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 38750398 Free PMC article.
-
PET imaging of sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs): Unveiling metabolic dynamics in diabetes and oncology.Mol Metab. 2024 Dec;90:102055. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.102055. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39454827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excretion of glucose analogue with SGLT2 affinity predicts response effectiveness to sodium glucose transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Aug;50(10):3034-3041. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06256-7. Epub 2023 May 17. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37195445 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
