Cancer Risk in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35903279
- PMCID: PMC9318815
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.937871
Cancer Risk in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: Research data suggest that patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis may increase the risk of cancer. However, existing research is inconsistent with this view. Therefore, to investigate the effect of Hashimoto's thyroiditis on the risk of developing cancer, we conducted this study.
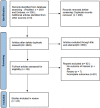
Methods: We searched the PubMed and Embase databases from database establishment until March 2022. After rigorous literature screening by two authors, 23 studies that met the inclusion criteria were identified, and the required data were independently extracted.
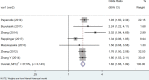
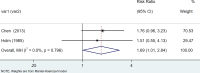
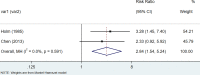
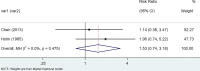
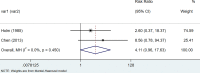
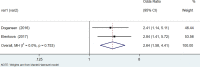
Results: We retrieved 3591 records, and after the screening, 11 case-control studies and 12 cohort studies were included in the analysis. Data analysis suggested that patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis had an increased risk of developing breast cancer, urogenital cancer, digestive organs cancer, hematologic cancer, and a low risk of respiratory cancers.
Conclusions: This systematic review and meta-analysis showed that patients with HT may have a significantly increased risk of thyroid cancer, breast cancers, lung cancer, digestive system cancer, urogenital cancers, blood cancers, and prolactinoma people without HT.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD 42022320741.
Keywords: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; cancer risk; meta-analysis; observational study; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Wang, Liang, Chen, Zhou, Fei, Yang and Que.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ralli M, Angeletti D, Fiore M, D'Aguanno V, Lambiase A, Artico M, et al. . Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: An Update on Pathogenic Mechanisms, Diagnostic Protocols, Therapeutic Strategies, and Potential Malignant Transformation. Autoimmun Rev (2020) 19(10):102649. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102649 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

