Clinical Manifestations and Genetic Influences in Sulfonamide-Induced Hypersensitivity
- PMID: 35903308
- PMCID: PMC9315057
- DOI: 10.2147/DHPS.S347522
Clinical Manifestations and Genetic Influences in Sulfonamide-Induced Hypersensitivity
Abstract
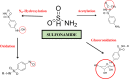
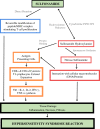
Drug hypersensitivity is an inflammatory or immune reaction induced by drugs. It can be fatal if not appropriately treated and cause the risk of long-term complications. Sulfonamides are classified as antimicrobial drugs with a broad spectrum effective for gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. This antibacterial agent works by competitively inhibiting folic acid synthesis, which prevents the growth and proliferation of microorganisms. In its use as antibiotics, sulfonamides can also cause adverse reactions in specific individuals. It has been widely reported that sulfonamide antimicrobials cause hypersensitivity reactions mediated by IgE or T cells. This review identifies symptoms or signs that can appear, as well as genes associated with sulfonamide hypersensitivity reactions, as sulfonamide may cause hypersensitivity in the form of uveitis, skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), parotitis, angioedema, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and pruritus. In addition, several genes were found to be associated with sulfonamide hypersensitivity, including HLA-A29, HLA-B12, HLA-DR7, HLA-B44, and HLA A*11:01.
Keywords: genetic influence; hypersensitivity; sulfonamide.
© 2022 Asyraf et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genotype-phenotype association between HLA and carbamazepine-induced hypersensitivity reactions: strength and clinical correlations.J Dermatol Sci. 2014 Feb;73(2):101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Dermatol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24268988
-
Sulfonamide Hypersensitivity: Fact and Fiction.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019 Sep-Oct;7(7):2116-2123. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2019.05.034. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019. PMID: 31495421 Review.
-
Sulfonamide Hypersensitivity.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022 Jun;62(3):400-412. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08872-3. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34212341 Review.
-
Sulfonamides.2017 Dec 5. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2017 Dec 5. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643703 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
[Severe skin reactions due to new medications].Hautarzt. 2018 Apr;69(4):278-289. doi: 10.1007/s00105-018-4153-2. Hautarzt. 2018. PMID: 29568997 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional Evaluation of Graphene Oxide-Sulfonamide Nanoconjugates: Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm, Cytocompatibility and Xenobiotic Metabolism Gene Expression Insight.Molecules. 2025 Jun 13;30(12):2585. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122585. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572550 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variations and Antibiotic-Related Adverse Events.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 2;17(3):331. doi: 10.3390/ph17030331. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of disseminated nocardia infection with initial symptoms manifesting as cognitive impairment: Case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 6;103(49):e39535. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039535. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39654166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and severe cutaneous allergic reactions to sulfonamides.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2024 Nov 1;45(6):e93-e100. doi: 10.2500/aap.2024.45.240086. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2024. PMID: 39517080 Free PMC article.
-
Causes of Drug-Induced Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction Epidermal Necrolysis (EN): An Analysis Using FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) Database.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Aug 16;16:2249-2257. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S422928. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37605788 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials