Serological Biomarkers of Intestinal Collagen Turnover Identify Early Response to Infliximab Therapy in Patients With Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 35903311
- PMCID: PMC9315105
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.933872
Serological Biomarkers of Intestinal Collagen Turnover Identify Early Response to Infliximab Therapy in Patients With Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background: Crohn's disease (CD) is characterized by excessive protease activity and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. To date, 30-50% of patients experience non-response to anti-TNF-α treatment. This study aimed to assess whether serological biomarkers of ECM turnover could monitor or predict response to infliximab (IFX) induction therapy in patients with and without a surgical history.
Methods: Serum biomarkers of type I (C1M), III (C3M), IV (C4M), and VI (C6Ma3) collagen degradation, type III (PRO-C3) and VI (PRO-C6) collagen formation, basement membrane turnover (PRO-C4), and T-cell activity (C4G), were measured at baseline and week 14, in 63 patients with CD undergoing IFX induction therapy. Patients were stratified according to surgical history.
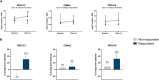
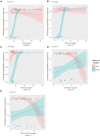
Results: C4M was elevated at baseline in responders with a surgical history (n = 10) and associated with response at baseline (P < 0.05). Additionally, C6Ma3, PRO-C3, and PRO-C6 were elevated at week 14 in responders compared with non-responders (n = 8) and could differentiate between the two groups (P < 0.05). Two biomarker ratios (C4M/C4G and PRO-C4/C4G) were elevated at week 14 in non-responders (n = 5) without a surgical history compared with responders (n = 40) and could differentiate between the response groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Baseline levels of a serological biomarker for type IV collagen degradation associated with response to IFX induction therapy, and biomarkers of type III and VI collagen formation may be used to monitor response at the end of induction therapy in patients with a surgical history. Biomarker ratios of type IV collagen turnover demonstrated promising results in monitoring treatment response in patients without a surgical history.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; TNF-α antagonists; biomarkers; collagen; fibrosis; infliximab; surgery.
Copyright © 2022 Alexdottir, Bourgonje, Karsdal, Pehrsson, Loveikyte, van Dullemen, Visschedijk, Festen, Weersma, Faber, Dijkstra and Mortensen.
Conflict of interest statement
MA, MP, MK, and JM are employees of Nordic Bioscience A/S. MK owns stocks in Nordic Bioscience A/S. GD received research grants from Royal DSM and speaker’s fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, Pfizer, and Abbvie. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chang JT. Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel diseases. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2652–64. - PubMed
-
- van Dullemen HM, van Deventer SJH, Hommes DW, Bijl HA, Jansen J, Tytgat GNJ, et al. Treatment of Crohn’s disease with anti-tumor necrosis factor chimeric monoclonal antibody (cA2). Gastroenterology. (1995) 109:129–35. - PubMed
-
- Plosker GL, Lyseng-Williamson KA. Adalimumab: in Crohn’s disease. BioDrugs. (2007) 21:125–32; discussion 133–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

