A review on benefits of quercetin in hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis
- PMID: 35903522
- PMCID: PMC9315272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.04.013
A review on benefits of quercetin in hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis
Abstract
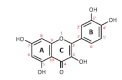
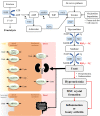
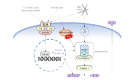
Hyperuricemia becomes a public health problem worldwide. It is not only a major risk factor for gout but also associated with the development of life-threatening diseases such as chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular diseases. Although there are several available therapeutic drugs, some serious adverse effects and contraindications are concerned. These drive the search for an alternative therapy that is effective and safe. Quercetin is of particular interesting since it has been reported numerous pharmacological activities, especially anti-hyperuricemia, antioxidant, anti-inflammation and amelioration of metabolic syndromes and cardiovascular diseases which are comorbidities of hyperuricemia and gout. In addition, quercetin has been widely used as a health supplement for many diseases however, the use for hyperuricemia and gout has not been indicated. Therefore, this review aims to gather and summarize published data regarding the efficacy in preclinical and clinical studies along with possible mechanism of action, and safety aspect of quercetin in order to support the use of quercetin as a dietary supplement for prevention and management of hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis and/or use as alternative or combination therapy to minimize the side effects of the conventional drugs.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Gout; Hyperuricemia; NLRP3 inflammasome; Quercetin.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Adachi S.-I., Oyama M., Kondo S., Yagasaki K. Comparative effects of quercetin, luteolin, apigenin and their related polyphenols on uric acid production in cultured hepatocytes and suppression of purine bodies-induced hyperuricemia by rutin in mice. Cytotechnology. 2021;73(3):343–351. doi: 10.1007/s10616-021-00452-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

