Enhanced abundance and activity of the chloroplast ATP synthase in rice through the overexpression of the AtpD subunit
- PMID: 35904136
- PMCID: PMC9629782
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erac320
Enhanced abundance and activity of the chloroplast ATP synthase in rice through the overexpression of the AtpD subunit
Abstract
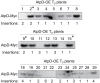
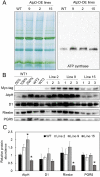
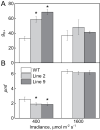
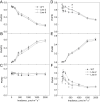
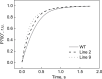
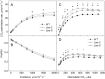
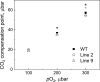
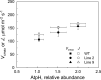
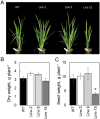
ATP, produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis, acts as the universal cellular energy cofactor fuelling all life processes. Chloroplast ATP synthase produces ATP using the proton motive force created by solar energy-driven thylakoid electron transport reactions. Here we investigate how increasing abundance of ATP synthase affects leaf photosynthesis and growth of rice, Oryza sativa variety Kitaake. We show that overexpression of AtpD, the nuclear-encoded subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase, stimulates both abundance of the complex, confirmed by immunodetection of thylakoid complexes separated by Blue Native-PAGE, and ATP synthase activity, detected as higher proton conductivity of the thylakoid membrane. Plants with increased AtpD content had higher CO2 assimilation rates when a stepwise increase in CO2 partial pressure was imposed on leaves at high irradiance. Fitting of the CO2 response curves of assimilation revealed that plants overexpressing AtpD had a higher electron transport rate (J) at high CO2, despite having wild-type-like abundance of the cytochrome b6f complex. A higher maximum carboxylation rate (Vcmax) and lower cyclic electron flow detected in transgenic plants both pointed to an increased ATP production compared with wild-type plants. Our results present evidence that the activity of ATP synthase modulates the rate of electron transport at high CO2 and high irradiance.
Keywords: ATP synthase; CO2 assimilation; electron transport; photosynthesis; proton motive force; thylakoid membrane.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures
References
-
- Capaldi RA, Aggeler R.. 2002. Mechanism of the F1F0-type ATP synthase, a biological rotary motor. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 27, 154–160. - PubMed
-
- Carmo-Silva E, Scales JC, Madgwick PJ, Parry MAJ.. 2015. Optimizing Rubisco and its regulation for greater resource use efficiency. Plant, Cell & Environment 38, 1817–1832. - PubMed
-
- Carrillo LR, Froehlich JE, Cruz JA, Savage LJ, Kramer DM.. 2016. Multi-level regulation of the chloroplast ATP synthase: the chloroplast NADPH thioredoxin reductase C (NTRC) is required for redox modulation specifically under low irradiance. The Plant Journal 87, 654–663. - PubMed
-
- Chida H, Nakazawa A, Akazaki H, et al. . 2007. Expression of the algal cytochrome c6 gene in Arabidopsis enhances photosynthesis and growth. Plant & Cell Physiology 48, 948–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

