The metabolic and molecular mechanisms of α‑mangostin in cardiometabolic disorders (Review)
- PMID: 35904170
- PMCID: PMC9354700
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5176
The metabolic and molecular mechanisms of α‑mangostin in cardiometabolic disorders (Review)
Abstract
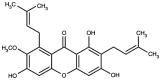
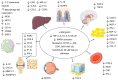
α‑mangostin is a xanthone predominantly encountered in Garcinia mangostana. Extensive research has been carried out concerning the effects of this compound on various diseases, including obesity, cancer and metabolic disorders. The present review suggests that α‑mangostin exerts promising anti‑obesity, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, cardioprotective, antioxidant and anti‑inflammatory effects on various pathways in cardiometabolic diseases. The anti‑obesity effects of α‑mangostin include the reduction of body weight and adipose tissue size, the increase in fatty acid oxidation, the activation of hepatic AMP‑activated protein kinase and Sirtuin‑1, and the reduction of peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor γ expression. Hepatoprotective effects have been revealed, due to reduced fibrosis through transforming growth factor‑β 1 pathways, reduced apoptosis and steatosis through reduced sterol regulatory‑element binding proteins expression. The antidiabetic effects include decreased fasting blood glucose levels, improved insulin sensitivity and the increased expression of GLUT transporters in various tissues. Cardioprotection is exhibited through the restoration of cardiac functions and structure, improved mitochondrial functions, the promotion of M2 macrophage populations, reduced endothelial and cardiomyocyte apoptosis and fibrosis, and reduced acid sphingomyelinase activity and ceramide depositions. The antioxidant effects of α‑mangostin are mainly related to the modulation of antioxidant enzymes, the reduction of oxidative stress markers, the reduction of oxidative damage through a reduction in Sirtuin 3 expression mediated by phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/protein kinase B/peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor‑γ coactivator‑1α signaling pathways, and to the increase in Nuclear factor‑erythroid factor 2‑related factor 2 and heme oxygenase‑1 expression levels. The anti‑inflammatory effects of α‑mangostin include its modulation of nuclear factor‑κB related pathways, the suppression of mitogen‑activated protein kinase activation, increased macrophage polarization to M2, reduced inflammasome occurrence, increased Sirtuin 1 and 3 expression, the reduced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, the production of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2, the reduced expression of Toll‑like receptors and reduced proinflammatory cytokine levels. These effects demonstrate that α‑mangostin may possess the properties required for a suitable candidate compound for the management of cardiometabolic diseases.
Keywords: Garcinia mangostana; metabolic syndrome; metabolism; obesity; xanthone; α-mangostin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A SIRT1 agonist reduces cognitive decline in type 2 diabetic rats through antioxidative and anti‑inflammatory mechanisms.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Feb;19(2):1040-1048. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9699. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30483738 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Garcinia mangostana and its Xanthones in Metabolic Syndrome and Related Complications.Phytother Res. 2017 Aug;31(8):1173-1182. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5862. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Phytother Res. 2017. PMID: 28656594 Review.
-
Silencing the Adipocytokine NOV: A Novel Approach to Reversing Oxidative Stress-Induced Cardiometabolic Dysfunction.Cells. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):3060. doi: 10.3390/cells11193060. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231029 Free PMC article.
-
Mangosteen xanthone γ-mangostin exerts lowering blood glucose effect with potentiating insulin sensitivity through the mediation of AMPK/PPARγ.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Dec;144:112333. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112333. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34678724
-
Mangiferin: a natural miracle bioactive compound against lifestyle related disorders.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 May 2;16(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0449-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28464819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Updating the Pharmacological Effects of α-Mangostin Compound and Unraveling Its Mechanism of Action: A Computational Study Review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Oct 24;18:4723-4748. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S478388. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39469723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demethylcalabaxanthone from Garcinia mangostana Exerts Antioxidant Effects through the Activation of the Nrf2 Pathway as Assessed via Molecular Docking and Biological Evaluation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 7;12(11):1980. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111980. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001833 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial-Protective Actions of Diethylether Extract from Gentiana kochiana and Xanthone Gentiacaulein Against Oxidized LDL-Induced Injury-In Vitro Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 5;26(3):1351. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031351. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941118 Free PMC article.
-
Sitosterol-rich Digera muricata against 7-ketocholesterol and lipopolysaccharide-mediated atherogenic responses by modulating NF-ΚB/iNOS signalling pathway in macrophages.3 Biotech. 2023 Oct;13(10):331. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03741-6. Epub 2023 Sep 3. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37670802 Free PMC article.
-
Pressurized Hot Water Extraction of Mangosteen Pericarp and Its Associated Molecular Signatures in Endothelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 30;12(11):1932. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111932. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grundy SM, Brewer HB, Jr, Cleeman JI, Smith SC, Jr, Lenfant C, American Heart Association National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the national heart, lung, and blood institute/American heart association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation. 2004;109:433–438. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000111245.75752.C6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

