Long non‑coding RNA CASC11 interacts with YBX1 to promote prostate cancer progression by suppressing the p53 pathway
- PMID: 35904175
- PMCID: PMC9374466
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5400
Long non‑coding RNA CASC11 interacts with YBX1 to promote prostate cancer progression by suppressing the p53 pathway
Erratum in
-
[Corrigendum] Long non‑coding RNA CASC11 interacts with YBX1 to promote prostate cancer progression by suppressing the p53 pathway.Int J Oncol. 2024 Jan;64(1):5. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5593. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38038145 Free PMC article.
Abstract
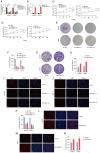
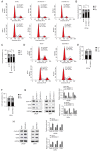
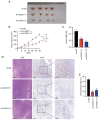
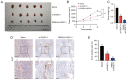
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the principal causes of cancer‑related death worldwide. The roles and mechanisms of long non‑coding RNA (lncRNA) involved in the development of PCa remain incompletely understood. The present study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of lncRNA in PCa tumorigenesis. In the present study, lncRNA cancer susceptibility candidate 11 (CASC11) was revealed to be a crucial regulator of PCa progression. The expression profiles of CASC11 in PCa were identified through analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus datasets, and validated in human PCa specimens and cell lines. Gain‑ and loss‑of‑function assays were utilized to explore the biological role of CASC11 in PCa initiation and progression. RNA‑sequencing, RNA pull‑down and RNA immunoprecipitation analyses were used to explore potential mechanisms with which CASC11 may be associated. Rescue experiments were further conducted to confirm this association. The present results revealed that CASC11 was dominantly distributed in the nuclei of PCa cells, and was highly expressed in PCa tissues and cells. Overexpression of CASC11 was markedly associated with increased tumor proliferation and migratory ability. Functionally, decreased proliferation and migration, as well as inhibited xenograft tumor growth, were observed in CASC11‑silenced PCa cells, whereas the opposite effects were detected in CASC11‑overexpressing cells. Mechanistically, CASC11 promoted progression of the cell cycle and competitively interacted with Y‑box binding protein 1 (YBX1) to block the p53 pathway. Given this, poly (β‑amino ester) (PBAE)/small interfering RNA‑CASC11 (si‑CASC11) nanoparticles were applied to inhibit CASC11 expression and enhance the antitumor effect in vivo. The results revealed that PBAE/si‑CASC11 nanoparticles augmented the antitumor efficacy of CASC11 knockdown in vivo. In conclusion, the present study suggested that CASC11 may regulate PCa progression and elucidated a novel CASC11/YBX1/p53 signaling axis, providing a potential lncRNA‑directed therapeutic strategy particularly for the treatment of patients with PCa.
Keywords: CASC11; Y‑box binding protein 1; p53 pathway; progression; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The previously uncharacterized lncRNA APP promotes prostate cancer progression by acting as a competing endogenous RNA.Int J Cancer. 2020 Jan 15;146(2):475-486. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32422. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31107971
-
CASC11 promotes aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells through miR-145/IGF1R axis.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021 Sep;24(3):891-902. doi: 10.1038/s41391-021-00353-0. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021. PMID: 33753875
-
LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 interacts with YBX1 to promote cancer progression by forming a positive feedback loop that activates FOXA1 transcription network.Theranostics. 2020 Aug 29;10(23):10823-10837. doi: 10.7150/thno.47830. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32929382 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SIRT7 in Prostate Cancer Progression: New Insight Into Potential Therapeutic Target.Cancer Med. 2025 Apr;14(7):e70786. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70786. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40165597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cells as Target for Prostate cancer Therapy: Opportunities and Challenges.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Dec;18(8):2833-2851. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10437-6. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35951166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Pathways in Breast Cancer Reprograming: An Insight to Non-Coding RNAs.Cells. 2022 Sep 23;11(19):2973. doi: 10.3390/cells11192973. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36230935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein L3 inhibits breast cancer proliferation and modulates cell cycle via the P53 pathway.J Cancer. 2024 Jul 2;15(14):4623-4635. doi: 10.7150/jca.96903. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39006089 Free PMC article.
-
VIM‑AS1 promotes proliferation and drives enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer via IGF2BP2‑mediated HMGCS1 mRNA stabilization.Int J Oncol. 2023 Mar;62(3):34. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5482. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36734275 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA CASC11 regulates the progress of delayed fracture healing via sponging miR-150-3p.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 14;19(1):757. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05226-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39543626 Free PMC article.
-
YBX1: an RNA/DNA-binding protein that affects disease progression.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 29;15:1635209. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1635209. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40799245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
