Endothelial Foxp1 Regulates Neointimal Hyperplasia Via Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1B Signal Pathway
- PMID: 35904197
- PMCID: PMC9375493
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026378
Endothelial Foxp1 Regulates Neointimal Hyperplasia Via Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1B Signal Pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Endothelial Foxp1 Regulates Neointimal Hyperplasia Via Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1B Signal Pathway.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Feb 21;12(4):e020899. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.020899. Epub 2023 Feb 15. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36789862 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
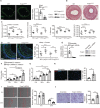
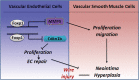
Background The endothelium is essential for maintaining vascular physiological homeostasis and the endothelial injury leads to the neointimal hyperplasia because of the excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Endothelial Foxp1 (forkhead box P1) has been shown to control endothelial cell (EC) proliferation and migration in vitro. However, whether EC-Foxp1 participates in neointimal formation in vivo is not clear. Our study aimed to investigate the roles and mechanisms of EC-Foxp1 in neointimal hyperplasia. Methods and Results The wire injury femoral artery neointimal hyperplasia model was performed in Foxp1 EC-specific loss-of-function and gain-of-function mice. EC-Foxp1 deletion mice displayed the increased neointimal formation through elevation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, and the reduction of EC proliferation hence reendothelialization after injury. In contrast, EC-Foxp1 overexpression inhibited the neointimal formation. EC-Foxp1 paracrine regulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via targeting matrix metalloproteinase-9. Also, EC-Foxp1 deletion impaired EC repair through reduction of EC proliferation via increasing cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1B expression. Delivery of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1B-siRNA to ECs using RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp)-peptide magnetic nanoparticle normalized the EC-Foxp1 deletion-mediated impaired EC repair and attenuated the neointimal formation. EC-Foxp1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-9/cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1B signaling pathway to control injury induced neointimal formation. Conclusions Our study reveals that targeting EC-Foxp1-matrix metalloproteinase-9/cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1B pathway might provide future novel therapeutic interventions for restenosis.
Keywords: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (Cdkn1b); matrix metalloproteinase‐9 (MMP9); neointimal formation; transcription factor forkhead box protein P1 (Foxp1).
Figures




References
-
- Chacko L, Howard JP, Rajkumar C, Nowbar AN, Kane C, Mahdi D, Foley M, Shun‐Shin M, Cole G, Sen S, et al. Effects of percutaneous coronary intervention on death and myocardial infarction stratified by stable and unstable coronary artery disease: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020;13:e006363. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006363 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

