Predictors and Outcomes of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Patients With a Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Above or Below 60
- PMID: 35904209
- PMCID: PMC9375469
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.122.025300
Predictors and Outcomes of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Patients With a Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Above or Below 60
Abstract
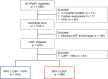
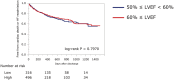
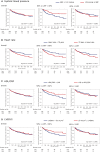
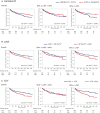
Background Although potential therapeutic candidates for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) are emerging, it is still unclear whether they will be effective in patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 60% or higher. Our aim was to identify the clinical characteristics of these patients with HFpEF by comparing them to patients with LVEF below 60%. Methods and Results From a multicenter, prospective, observational cohort (PURSUIT-HFpEF [Prospective Multicenter Obsevational Study of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction]), we investigated 812 consecutive patients (median age, 83 years; 57% women), including 316 with 50% ≤ LVEF <60% and 496 with 60% ≤ LVEF, and compared the clinical backgrounds of the 2 groups and their prognoses for cardiac mortality or HF readmission. Two hundred four adverse outcomes occurred at a median of 366 days. Multivariable Cox regression tests adjusted for age, sex, heart rate, atrial fibrillation, estimated glomerular filtration rate, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, and prior heart failure hospitalization revealed that systolic blood pressure (hazard ratio [HR], 0.925 [95% CI, 0.862-0.992]; P=0.028), high-density lipoprotein to C-reactive protein ratio (HR, 0.975 [95% CI, 0.944-0.995]; P=0.007), and left ventricular end-diastolic volume index (HR, 0.870 [95% CI, 0.759-0.997]; P=0.037) were uniquely associated with outcomes among patients with 50% ≤ LVEF <60%, whereas only the ratio of peak early mitral inflow velocity to velocity of mitral annulus early diastolic motion e'(HR, 1.034 [95% CI, 1.003-1.062]; P=0.034) was associated with outcomes among patients with 60% ≤ LVEF. Conclusions Prognostic factors show distinct differences between patients with HFpEF with 50% ≤ LVEF <60% and with 60% ≤ LVEF. These findings suggest that the 2 groups have different inherent pathophysiology. Registration URL: https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi-open-bin/ctr_e/ctr_view.cgi?recptno=R000024414; Unique identifier: UMIN000021831 PURSUIT-HFpEF.
Keywords: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; left ventricular ejection fraction; prognostic factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic Importance of Right Ventricular-Vascular Uncoupling in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Nov;13(11):e011430. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.120.011430. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33198494
-
Prognostic Importance of Pulmonary Arterial Capacitance in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Oct 19;10(20):e023043. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023043. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34612057 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Features of Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Dec 10;74(23):2858-2873. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.063. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31806129 Clinical Trial.
-
Correlation with invasive left ventricular filling pressures and prognostic relevance of the echocardiographic diastolic parameters used in the 2016 ESC heart failure guidelines and in the 2016 ASE/EACVI recommendations: a systematic review in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Sep;20(9):1303-1311. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1220. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29877602
-
Multi-modality assessment of congestion in acute heart failure: Associations with left ventricular ejection fraction and prognosis.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Mar;49(3):102374. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102374. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38185433 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of left ventricular strain-volume loop characteristics with adverse events in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Aug 23;24(9):1168-1176. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jead117. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37259911 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of atrial fibrillation on clinical outcomes in heart failure with mid-range and preserved ejection fraction patients.Heart Rhythm. 2024 Nov;21(11):2110-2117. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2024.05.039. Epub 2024 May 24. Heart Rhythm. 2024. PMID: 38797306 Clinical Trial.
-
[Left Ventricular Structural and Functional Changes in Obese Subjects With Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction After Bariatric Surgery: Assessment With Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Nov 20;55(6):1410-1417. doi: 10.12182/20241160503. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39990850 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Time to Reconsider Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure: Reclassification Needed Beyond Ejection Fraction.JACC Asia. 2023 Aug 22;3(5):752-754. doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2023.07.001. eCollection 2023 Oct. JACC Asia. 2023. PMID: 38094993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vaduganathan M, Claggett BL, Jhund PS, Cunningham JW, Pedro Ferreira J, Zannad F, Packer M, Fonarow GC, McMurray JJV, Solomon SD. Estimating lifetime benefits of comprehensive disease‐modifying pharmacological therapies in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a comparative analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2020;396:121–128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30748-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bozkurt B, Coats AJS, Tsutsui H, Abdelhamid CM, Adamopoulos S, Albert N, Anker SD, Atherton J, Böhm M, Butler J, et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: a report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure: endorsed by the Canadian Heart Failure Society, Heart Failure Association of India, Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and Chinese Heart Failure Association. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23:352–380. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2115 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ho JE, Enserro D, Brouwers FP, Kizer JR, Shah SJ, Psaty BM, Bartz TM, Santhanakrishnan R, Lee DS, Chan C, et al. Predicting heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction: the International Collaboration on Heart Failure Subtypes. Circ Heart Fail. 2016;9:e003116. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.003116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

