Sexually dimorphic distribution of kiss1 and kiss2 in the brain of yellowtail clownfish, Amphiprion clarkii
- PMID: 35904230
- PMCID: PMC9346329
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-22-0136
Sexually dimorphic distribution of kiss1 and kiss2 in the brain of yellowtail clownfish, Amphiprion clarkii
Abstract
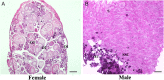
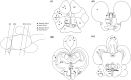
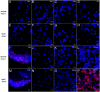
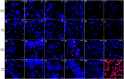
Kisspeptin system was shown to be a key factor in mediating social stress and reproduction. Yellowtail clownfish, Amphiprion clarkii, is a hermaphrodite fish, whose sex determination and gonadal development are affected by the social status of individuals. The yellowtail clownfish is a fantastic animal model to explore sex determination, but the social status and precise distribution of kiss mRNAs in the brain of this species are unknown. Hererin, a novel in situ hybridization technique, RNAscope, was used to investigate the distribution of kiss1 and kiss2 expressions in the brain of yellowtail clownfish. The coronal planes of brain showed that the kiss1 signal was mainly present in dorsal habenular nucleus (NHd) and kiss2 mRNA was widely expressed in telencephalon, midbrain, and hypothalamus, especially in dorsal part of the nucleus of the lateral recess (NRLd). Additionally, kiss1 and kiss2 signals have sexually dimorphic distribution. The kiss1 mRNA was distributed in NHd, the telencephalon, and lateral part of the diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe (NDLIl) of females but in NHd and NDLIl of males. kiss2 signals were stronger in females than that in males. The distribution of kiss1 and kiss2 neurons in NHd of habenula and NRLd of hypothalamus may suggest that kiss genes associate environmental signaling and reproductive function in yellowtail clownfish.
Keywords: RNAscope; kisspeptin; sexually dimorphic distribution; social stress; yellowtail clownfish.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of the kiss2 promoter in yellowtail clownfish (Amphiprion clarkii) by cortisol via GRE-dependent GR pathway.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 3;13:902737. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.902737. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35992144 Free PMC article.
-
Kiss2 but not kiss1 is involved in the regulation of social stress on the gonad development in yellowtail clownfish, Amphiprion clarkii.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2020 Nov 1;298:113551. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2020.113551. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32687936
-
Molecular characterization, tissue distribution, and mRNA expression profiles of two Kiss genes in the adult male and female chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) during different gonadal stages.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010 Oct;169(1):28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.07.011. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20691652
-
Biological Significance of Kisspeptin-Kiss 1 Receptor Signaling in the Habenula of Teleost Species.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 May 7;9:222. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00222. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29867758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three types of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurones and steroid-sensitive sexually dimorphic kisspeptin neurones in teleosts.J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Mar;21(4):334-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01850.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19210296 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the kiss2 promoter in yellowtail clownfish (Amphiprion clarkii) by cortisol via GRE-dependent GR pathway.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 3;13:902737. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.902737. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35992144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu F, Zhang X, Zhang W, Huang B, Liu Z, Hu C, Wang D. Expression of three gonadotropin subunits in Southern catfish gonad and their possible roles during early gonadal development. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology: Part A, Molecular and Integrative Physiology 200915344–48. (10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.12.013) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

