Mitigation of Multi-Organ Radiation Injury with ACE2 Agonist Diminazene Aceturate
- PMID: 35904437
- PMCID: PMC9641750
- DOI: 10.1667/RADE-22-00055.1
Mitigation of Multi-Organ Radiation Injury with ACE2 Agonist Diminazene Aceturate
Abstract
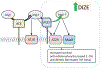
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is known to regulate the pathogenesis of radiation-induced injury as inhibitors of the RAS enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) have established function as mitigators of multi-organ radiation injury. To further elucidate the role of RAS signaling during both the acute and delayed syndromes of radiation exposure, we have evaluated whether pharmacologic modulation of alternate RAS enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) reduces the pathogenesis of multi-organ radiation-induced injuries. Here, we demonstrate pharmacologic ACE2 activation with the small molecule ACE2 agonist diminazene aceturate (DIZE) improves survival in rat models of both hematologic acute radiation syndrome (H-ARS) and multi-organ delayed effects of acute radiation exposure (DEARE). In the H-ARS model, DIZE treatment increased 30-day survival by 30% compared to vehicle control rats after a LD50/30 total-body irradiation (TBI) dose of 7.75 Gy. In the mitigation of DEARE, ACE2 agonism with DIZE increased median survival by 30 days, reduced breathing rate, and reduced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels compared to control rats after partial-body irradiation (PBI) of 13.5 Gy. DIZE treatment was observed to have systemic effects which may explain the multi-organ benefits observed including mobilization of hematopoietic progenitors to the circulation and a reduction in plasma TGF-beta levels. These data suggest the ACE2 enzyme plays a critical role in the RAS-mediated pathogenesis of radiation injury and may be a potential therapeutic target for the development of medical countermeasures for acute radiation exposure.
©2022 by Radiation Research Society. All rights of reproduction in any form reserved.
Figures



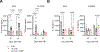

References
-
- van der Veen SJ, Ghobadi G, de Boer RA, Faber H, Cannon MV, Nagle PW, et al. ACE inhibition attenuates radiation-induced cardiopulmonary damage. Radiother Oncol 2015; 114, 96–103. - PubMed
-
- Ryu S, Kolozsvary A, Jenrow KA, Brown SL, Kim JH. Mitigation of radiation-induced optic neuropathy in rats by ACE inhibitor ramipril: importance of ramipril dose and treatment time. J Neurooncol 2007; 82, 119–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

