Epithelial HVEM maintains intraepithelial T cell survival and contributes to host protection
- PMID: 35905286
- PMCID: PMC9422995
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abm6931
Epithelial HVEM maintains intraepithelial T cell survival and contributes to host protection
Abstract
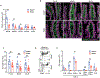
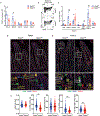
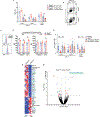
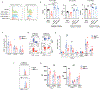
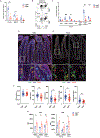
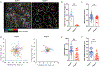
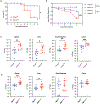
Intraepithelial T cells (IETs) are in close contact with intestinal epithelial cells and the underlying basement membrane, and they detect invasive pathogens. How intestinal epithelial cells and basement membrane influence IET survival and function, at steady state or after infection, is unclear. The herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM), a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, is constitutively expressed by intestinal epithelial cells and is important for protection from pathogenic bacteria. Here, we showed that at steady-state LIGHT, an HVEM ligand, binding to epithelial HVEM promoted the survival of small intestine IETs. RNA-seq and addition of HVEM ligands to epithelial organoids indicated that HVEM increased epithelial synthesis of basement membrane proteins, including collagen IV, which bound to β1 integrins expressed by IETs. Therefore, we proposed that IET survival depended on β1 integrin binding to collagen IV and showed that β1 integrin-collagen IV interactions supported IET survival in vitro. Moreover, the absence of β1 integrin expression by T lymphocytes decreased TCR αβ+ IETs in vivo. Intravital microscopy showed that the patrolling movement of IETs was reduced without epithelial HVEM. As likely consequences of decreased number and movement, protective responses to Salmonella enterica were reduced in mice lacking either epithelial HVEM, HVEM ligands, or β1 integrins. Therefore, IETs, at steady state and after infection, depended on HVEM expressed by epithelial cells for the synthesis of collagen IV by epithelial cells. Collagen IV engaged β1 integrins on IETs that were important for their maintenance and for their protective function in mucosal immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
HVEM signalling at mucosal barriers provides host defence against pathogenic bacteria.Nature. 2012 Aug 9;488(7410):222-5. doi: 10.1038/nature11242. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22801499 Free PMC article.
-
Intraepithelial T Cells Diverge by Intestinal Location as Pigs Age.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 16;11:1139. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01139. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32612605 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal expression of the TNF family receptor herpes virus entry mediator and its ligand LIGHT on activated T cells: LIGHT down-regulates its own receptor.J Immunol. 2000 Oct 15;165(8):4397-404. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.8.4397. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11035077
-
HVEM is a TNF Receptor with Multiple Regulatory Roles in the Mucosal Immune System.Immune Netw. 2014 Apr;14(2):67-72. doi: 10.4110/in.2014.14.2.67. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Immune Netw. 2014. PMID: 24851095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CD160, BTLA, LIGHT/HVEM pathway: a bidirectional switch regulating T-cell activation.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):244-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00783.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426226 Review.
Cited by
-
Intravital Imaging of Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes.Bio Protoc. 2023 Jul 20;13(14):e4720. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4720. eCollection 2023 Jul 20. Bio Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37497460 Free PMC article.
-
Ligands for Intestinal Intraepithelial T Lymphocytes in Health and Disease.Pathogens. 2025 Jan 23;14(2):109. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020109. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xylan Prebiotics and the Gut Microbiome Promote Health and Wellbeing: Potential Novel Roles for Pentosan Polysulfate.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 16;15(9):1151. doi: 10.3390/ph15091151. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Mucosal Immune Barrier: A Powerful Firewall Against Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury via the Gut-Lung Axis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr 10;17:2173-2193. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S448819. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38617383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically predicted N-methylhydroxyproline levels mediate the association between naive CD8+ T cells and allergic rhinitis: a mediation Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 May 23;15:1396246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396246. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38846949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edelblum KL, Shen L, Weber CR, Marchiando AM, Clay BS, Wang Y, Prinz I, Malissen B, Sperling AI, Turner JR, Dynamic migration of gammadelta intraepithelial lymphocytes requires occludin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109, 7097–7102 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

