Intra-articular triamcinolone hexacetonide injections in hands osteoarthritis ‒ A double-blinded randomized controlled trial with a one year follow-up
- PMID: 35905573
- PMCID: PMC9335385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100036
Intra-articular triamcinolone hexacetonide injections in hands osteoarthritis ‒ A double-blinded randomized controlled trial with a one year follow-up
Abstract
Objective: to evaluate the effectiveness of triamcinolone Hexacetonide (TH) Intra-Articular Injection (IAI) in hand Interphalangeal Joints (IP) of Osteoarthritis (OA) patients to improve pain and joint swelling; improve function, goniometry, and grasping force, and assess IAI influence on radiographic evolution over 1-year.
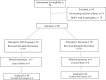
Methods: A randomized, double-blind study. 60 patients who underwent IAI at the most symptomatic IP joint were randomly assigned to receive TH+Lidocaine (LD) (TH/LD group) or just LD (LD group). Patients were assessed blindly for 1-year, at baseline and 1, 4, 8, 12, and 48 weeks. The following variables were assessed: articular pain and swelling, AUSCAN and COCHIN functional questionnaires, grip and pinch strength, goniometry, perception of improvement, acetaminophen consumption, and simple radiography. Repeated-measures ANOVA test was used to analyze the intervention response.
Results: Sixty patients completed the follow-up. There were nine missed assessments. 97% were women; mean age of 61-years (SD = 8.2), and approximately 5-years of disease (SD = 3.6). Half of the patients present radiographic classification Kellgren and Lawrence (KL) grades I and II, and the other half grades III and IV. The two groups evolved similarly at 48-weeks. TH/LD group had a better evaluation in joint swelling and acetaminophen consumption (p = 0.04 and p < 0.001, respectively) at 48-weeks. Radiographically there was no statistical difference between groups (KL, p = 0.564; erosive OA, p = 0.999; worsening, p = 0.573).
Conclusion: The IAI IP hands OA is effective for the improvement of joint swelling and decrease of analgesic consumption and does not influence the radiographic evolution of the injected joint.
Keywords: Corticosteroid; Hands; Intra-articular injection; Osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2022 HCFMUSP. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kloppenburg M, Boyesen P, Smeets W, Haugen I, Liu R, Visser W, et al. Report from the OMERACT hand osteoarthritis special interest group: advances and future research priorities. J Rheumatol. 2014;41:810–818. - PubMed
-
- Roemer FW, Eckstein F, Hayashi D, Guermazi A. The role of imaging in osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28:31–60. - PubMed
-
- Mahendira D, Towheed TE. Systematic review of non-surgical therapies for osteoarthritis of the hand: an update. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2009;17:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Dougados M. In: Rheumatology. 4th ed. Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, editors. Elsevier; Mosby: 2007. Management of limb osteoarthritis; pp. 1753–1763.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials