A multi-layer strip ionization chamber (MLSIC) device for proton pencil beam scan quality assurance
- PMID: 35905730
- PMCID: PMC11000494
- DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac8593
A multi-layer strip ionization chamber (MLSIC) device for proton pencil beam scan quality assurance
Abstract
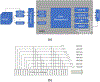
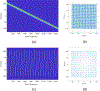
Objective. Proton pencil beam scanning (PBS) treatment fields needs to be verified before treatment deliveries to ensure patient safety. In current practice, treatment beam quality assurance (QA) is measured at a few selected depths using film or a 2D detector array, which is insensitive and time-consuming. A QA device that can measure all key dosimetric characteristics of treatment beams spot-by-spot within a single beam delivery is highly desired.Approach. We developed a multi-layer strip ionization chamber (MLSIC) prototype device that comprises of two layers of strip ionization chambers (IC) plates for spot position measurement and 64 layers of plate IC for beam energy measurement. The 768-channel strip ion chamber signals are integrated and sampled at a speed of 3.125 kHz. It has a 25.6 cm × 25.6 cm maximum measurement field size and 2 mm spatial resolution for spot position measurement. The depth resolution and maximum depth were 2.91 mm and 18.6 cm for 1.6 mm thick IC plate, respectively. The relative weight of each spot was determined from total charge by all IC detector channels.Main results. The MLSIC is able to measure ionization currents spot-by-spot. The depth dose measurement has a good agreement with the ground truth measured using a water tank and commercial one-dimensional (1D) multi-layer plate chamber. It can verify the spot position, energy, and relative weight of clinical PBS beams and compared with the treatment plans.Significance. The MLSIC is a highly efficient QA device that can measure the key dosimetric characteristics of proton treatment beams spot-by-spot with a single beam delivery. It may improve the quality and efficiency of clinical proton treatments.
Keywords: intensity modulated proton therapy; multilayer ionization chamber; proton therapy; quality assurance.
© 2022 Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine.
Figures
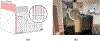


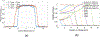



References
-
- Arjomandy B et al. 2019. AAPM task group 224: comprehensive proton therapy machine quality assurance Med. Phys. 46 6–8 - PubMed
-
- Arjomandy B, Sahoo N, Ding X and Gillin M 2008. Use of a two-dimensional ionization chamber array for proton therapy beam quality assurance Med. Phys. 35 3889–94 - PubMed
-
- Besl PJ and McKay ND 1992. A method for registration of 3D shapes IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14 239–56
-
- Bizzocchi N, Fracchiolla F, Schwarz M and Algranati C 2017. A fast and reliable method for daily quality assurance in spot scanning proton therapy with a compact and inexpensive phantom Med. Dosim. 42 238–46 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
