An experimental evaluation of the efficacy of perinatal sulforaphane supplementation to decrease the incidence and severity of vinclozolin-induced hypospadias in the mouse model
- PMID: 35905821
- PMCID: PMC9450412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116177
An experimental evaluation of the efficacy of perinatal sulforaphane supplementation to decrease the incidence and severity of vinclozolin-induced hypospadias in the mouse model
Abstract
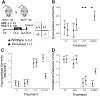
Determining the mechanisms of toxicity induced by pollutants has long been a research priority in lieu of considering the mechanisms of resilience that prevent deleterious impacts. Protective mechanisms in many taxa can be therapeutically targeted to enhance resilience to synthetic toxicants. For example, the environmental sensor, Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nfe2l2 or Nrf2), a transcription factor, facilitates transcription of many protective genes. Hypospadias is a common malformation of the penis. The risk of being born with hypospadias increases with pollutant exposure. We use vinclozolin-induced hypospadias in the mouse as a model to test the hypothesis that pollutant-induced birth defects can be prevented and reduced in severity by augmenting natural mechanisms of resilience. Pregnant mice were exposed to the demasculinizing toxicant, vinclozolin, in combination with increasing doses of the NRF2 activator, sulforaphane. The sulforaphane dose that most effectively increased masculinization (anogenital distance) was identified and used to test the hypothesis that sulforaphane reduces the hypospadias-inducing potency of vinclozolin. Finally, a Nrf2 knockout study was conducted to test whether NRF2 was required for the sulforaphane-induced rescue effects. Sulforaphane supplementation to vinclozolin exposed embryos increased anogenital distance in a nonlinear fashion typical of Nrf2 activators. The most effective dose of sulforaphane (45 mg/kg) reduced the occurrence and severity of vinclozolin-induced hypospadias and corrected penis morphogenesis. The sulforaphane-induced rescue effect was dependent on the presence of Nrf2. Nrf2 plays a critical role in protecting the fetus from vinclozolin and reduces the incidence and severity of hypospadias, the most common birth defect in boys in many countries. This work lays a foundation for developing prenatal supplements that will protect the fetus from pollutant-induced hypospadias. Studying the protective mechanisms that drive resilience to toxicants will facilitate innovation of protective therapies.
Keywords: Birth defects prevention; Hypospadias; Mechanisms of resilience; Preventive toxicology; Sulforaphane; Vinclozolin.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
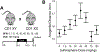
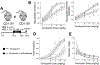
Similar articles
-
Endocrine disruptors and hypospadias: role of genistein and the fungicide vinclozolin.Urology. 2007 Sep;70(3):618-21. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.05.004. Urology. 2007. PMID: 17905137
-
Nrf2 Activation Attenuates Acrylamide-Induced Neuropathy in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 1;22(11):5995. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115995. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206048 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-arthritis effect of sulforaphane, an activator of Nrf2, is associated with inhibition of both B cell differentiation and the production of inflammatory cytokines.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 16;16(2):e0245986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245986. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33592002 Free PMC article.
-
The phytoprotective agent sulforaphane prevents inflammatory degenerative diseases and age-related pathologies via Nrf2-mediated hormesis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105283. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105283. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33160067 Review.
-
Sulforaphane and Other Nutrigenomic Nrf2 Activators: Can the Clinician's Expectation Be Matched by the Reality?Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7857186. doi: 10.1155/2016/7857186. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26881038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sulforaphane protects developing neural networks from VPA-induced synaptic alterations.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Sep;30(9):3868-3884. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-02967-5. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40175519 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

