Neprilysins regulate muscle contraction and heart function via cleavage of SERCA-inhibitory micropeptides
- PMID: 35906206
- PMCID: PMC9338278
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31974-1
Neprilysins regulate muscle contraction and heart function via cleavage of SERCA-inhibitory micropeptides
Abstract
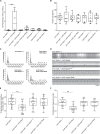
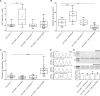
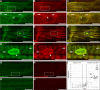
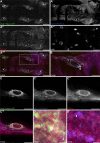
Muscle contraction depends on strictly controlled Ca2+ transients within myocytes. A major player maintaining these transients is the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase, SERCA. Activity of SERCA is regulated by binding of micropeptides and impaired expression or function of these peptides results in cardiomyopathy. To date, it is not known how homeostasis or turnover of the micropeptides is regulated. Herein, we find that the Drosophila endopeptidase Neprilysin 4 hydrolyzes SERCA-inhibitory Sarcolamban peptides in membranes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, thereby ensuring proper regulation of SERCA. Cleavage is necessary and sufficient to maintain homeostasis and function of the micropeptides. Analyses on human Neprilysin, sarcolipin, and ventricular cardiomyocytes indicates that the regulatory mechanism is evolutionarily conserved. By identifying a neprilysin as essential regulator of SERCA activity and Ca2+ homeostasis in cardiomyocytes, these data contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the complex mechanisms that control muscle contraction and heart function in health and disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

