A 19 day earth tide measurement with a MEMS gravimeter
- PMID: 35906251
- PMCID: PMC9338064
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16881-1
A 19 day earth tide measurement with a MEMS gravimeter
Abstract
The measurement of tiny variations in local gravity enables the observation of subterranean features. Gravimeters have historically been extremely expensive instruments, but usable gravity measurements have recently been conducted using MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) sensors. Such sensors are cheap to produce, since they rely on the same fabrication techniques used to produce mobile phone accelerometers. A significant challenge in the development of MEMS gravimeters is maintaining stability over long time periods, which is essential for long term monitoring applications. A standard way to demonstrate gravimeter stability and sensitivity is to measure the periodic elastic distortion of the Earth due to tidal forces-the Earth tides. Here, a 19 day measurement of the Earth tides, with a correlation coefficient to the theoretical signal of 0.975, has been presented. This result demonstrates that this MEMS gravimeter is capable of conducting long-term time-lapse gravimetry, a functionality essential for applications such as volcanology.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
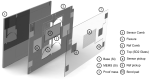
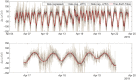

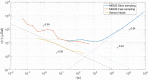
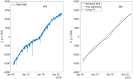
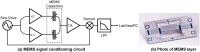
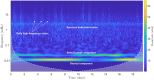
References
-
- Barnes G, Barraud J. Imaging geologic surfaces by inverting gravity gradient data with depth horizons. Geophysics. 2012;77:G1–G11. doi: 10.1190/geo2011-0149.1. - DOI
-
- Rim H, Li Y. Advantages of borehole vector gravity in density imaging. Geophysics. 2015;80:G1–G13. doi: 10.1190/geo2013-0394.1. - DOI
-
- Kaufmann G. Geophysical mapping of solution and collapse sinkholes. Appl. Geophys. 2014;111:271–288. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2014.10.011. - DOI
-
- Butler D. Microgravimetric and gravity gradient techniques for detection of subsurface cavities. Geophysics. 1984;49:1084–1096. doi: 10.1190/1.1441723. - DOI
-
- Romaides A, et al. A comparison of gravimetric techniques for measuring subsurface void signals. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001;34:433–443. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/34/3/331. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

