Decreased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) in cord blood monocytes under anoxia
- PMID: 35906309
- PMCID: PMC10033401
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-022-02193-7
Decreased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) in cord blood monocytes under anoxia
Abstract
Background: Infections are a major cause for morbidity and mortality in neonates; however, the underling mechanisms for increased infection susceptibility are incompletely understood. Hypoxia, which is present in inflamed tissues, has been identified as an important activation signal for innate immune cells in adults and is mainly mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α). Fetal tissue pO2 physiologically is low but rises immediately after birth.
Methods: In this study, the effect of low oxygen partial pressure (pO2) on HIF-1α expression and its targets phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion was compared in vitro between immune cells from adult peripheral blood and cord blood using anoxia, HIF-1α stabilizer desferroxamin (DFO) and E. coli as stimuli.
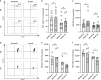
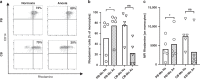
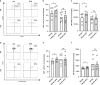
Results: We show that anoxia-induced HIF-1α protein accumulation, phagocytosis, ROS-production and VEGF-expression were greatly diminished in cord blood compared to adult cells. E. coli led to HIF-1α gene expression in adult and cord blood immune cells; however, cord blood cells failed to accumulate HIF-1α protein and VEGF upon E. coli stimulation.
Conclusions: Taken together, our results show a diminished activation of cord blood immune cells by low pO2, which might contribute to impaired reactivity in the context of infection.
Impact: Neonatal immune cells do not accumulate HIF-1α under low oxygen partial pressure leading to decreased phagocytosis and decreased ROS production. We demonstrate a previously unknown mechanism of reduced activation of neonatal immune cells in the context of an inflammatory response. This could contribute to the increased susceptibility of newborns and preterm infants to infection.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
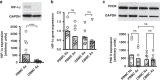

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

