Incremental monounsaturated to saturated fat ratio and fibre consumption is associated with a reduction in a composite score of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: Prospective results from the Moli-sani study
- PMID: 35906332
- PMCID: PMC9336117
- DOI: 10.1038/s41430-022-01185-4
Incremental monounsaturated to saturated fat ratio and fibre consumption is associated with a reduction in a composite score of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: Prospective results from the Moli-sani study
Abstract
Background/objectives: Unsaturated fats, fibre-rich foods and polyphenols are distinctive features of a traditional Mediterranean diet and have pleiotropic properties possibly contributing to reduce the long-term risk of non-communicable diseases and mortality associated with this diet. We aimed to evaluate whether changes over time in dietary fats, fibre and polyphenols consumption are associated with modifications in cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors.
Methods: The analytic sample consists of a sub-cohort of 2023 men and women enrolled in the Moli-sani Study (n = 24,325). Dietary and health data were obtained both at baseline (2005-2010) and at re-examination (2017-2020). The exposures were changes in dietary fats, fibre and polyphenols consumption measured after 12.7 years (median), and the outcome was change in a composite score including 13 modifiable CVD risk factors (e.g., blood lipids, C-reactive protein), measured both at enrolment and after the 12.7 years period.
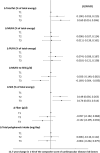
Results: In multivariable-adjusted analysis including lifestyles, sociodemographic and clinical factors, an incremental intake of the ratio of monounsaturated to saturated fats or of fibre was associated with a reduction in the composite score of CVD risk factors (β = -0.086; 95%CI -0.150, -0.021 and β = -0.051; 95%CI -0.091, -0.012, respectively). Change in polyphenol intake was not associated with a substantial variation in the CVD risk score (p = 0.15).
Conclusions: An incremental consumption over time of monounsaturated versus saturated fats and of fibre was associated with an improvement in modifiable CVD risk factors as reflected by a composite score.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. 2020. Scientific Report of the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee: Advisory Report to the Secretary of Agriculture and the Secretary of Health and Human Services. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

