Molecular Alterations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Hope for Effective Treatment by Targeting YAP
- PMID: 35906513
- PMCID: PMC9345804
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-022-00900-2
Molecular Alterations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Hope for Effective Treatment by Targeting YAP
Abstract
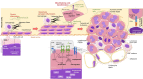
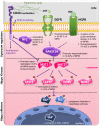
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive neoplasm, which has primarily been attributed to the exposure to asbestos fibers (83% of cases); yet, despite a ban of using asbestos in many countries, the incidence of malignant pleural mesothelioma failed to decline worldwide. While little progress has been made in malignant pleural mesothelioma diagnosis, bevacizumab at first, then followed by double immunotherapy (nivolumab plus ipilumumab), were all shown to improve survival in large phase III randomized trials. The morphological analysis of the histological subtyping remains the primary indicator for therapeutic decision making at an advanced disease stage, while a platinum-based chemotherapy regimen combined with pemetrexed, either with or without bevacizumab, is still the main treatment option. Consequently, malignant pleural mesothelioma still represents a significant health concern owing to poor median survival (12-18 months). Given this context, both diagnosis and therapy improvements require better knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying malignant pleural mesothelioma's carcinogenesis and progression. Hence, the Hippo pathway in malignant pleural mesothelioma initiation and progression has recently received increasing attention, as the aberrant expression of its core components may be closely related to patient prognosis. The purpose of this review was to provide a critical analysis of our current knowledge on these topics, the main focus being on the available evidence concerning the role of each Hippo pathway's member as a promising biomarker, enabling detection of the disease at earlier stages and thus improving prognosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Fatéméh Dubois, Céline Bazille, Jérôme Levallet, Elodie Maille, Solenn Brosseau, Jeannick Madelaine, Emmanuel Bergot, Gérard Zalcman, and Guénaëlle Levallet have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet. 2016 Apr 2;387(10026):1405-1414. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01238-6. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 26719230 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of bevacizumab in the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma.Future Oncol. 2017 Dec;13(28):2537-2546. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0307. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29086616 Review.
-
Targeting angiogenesis for patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma.Semin Oncol. 2019 Apr;46(2):145-154. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Semin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31280996 Review.
-
The effectiveness and safety of platinum-based pemetrexed and platinum-based gemcitabine treatment in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma.BMC Cancer. 2015 Jul 9;15:510. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1519-z. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26156324 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gemcitabine and vinorelbine as second-line or beyond treatment in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma pretreated with platinum plus pemetrexed chemotherapy.Int J Clin Oncol. 2014 Aug;19(4):601-6. doi: 10.1007/s10147-013-0619-5. Epub 2013 Oct 26. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24158772
Cited by
-
Identification of a novel prognostic gene signature in pleural mesothelioma: a study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas database and experimental validation.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):2981-2998. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2531. Epub 2025 May 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530124 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant pleural mesothelioma: The disdained member of thoracic oncology!World J Exp Med. 2024 Sep 20;14(3):91739. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i3.91739. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. World J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39312698 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pH sensitive theranostic PLGA nanoparticle for boron neutron capture therapy in mesothelioma treatment.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 12;13(1):620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27625-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36635364 Free PMC article.
-
YAP/TEAD4/SP1-induced VISTA expression as a tumor cell-intrinsic mechanism of immunosuppression in colorectal cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2025 May;32(5):911-925. doi: 10.1038/s41418-025-01446-2. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 39875519 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Next Generation Sequencing Application in Mesothelioma: Finding a Golden Needle in the Haystack.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;15(24):5716. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245716. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

