Management of arthrofibrosis in neuromuscular disorders: a review
- PMID: 35906570
- PMCID: PMC9336011
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05677-z
Management of arthrofibrosis in neuromuscular disorders: a review
Abstract
Arthrofibrosis, or rigid contracture of major articular joints, is a significant morbidity of many neurodegenerative disorders. The pathogenesis depends on the mechanism and severity of the precipitating neuromuscular disorder. Most neuromuscular disorders, whether spastic or hypotonic, culminate in decreased joint range of motion. Limited range of motion precipitates a cascade of pathophysiological changes in the muscle-tendon unit, the joint capsule, and the articular cartilage. Resulting joint contractures limit functional mobility, posing both physical and psychosocial burdens to patients, economic burdens on the healthcare system, and lost productivity to society. This article reviews the pathophysiology of arthrofibrosis in the setting of neuromuscular disorders. We describe current non-surgical and surgical interventions for treating arthrofibrosis of commonly affected joints. In addition, we preview several promising modalities under development to ameliorate arthrofibrosis non-surgically and discuss limitations in the field of arthrofibrosis secondary to neuromuscular disorders.
Keywords: Contractures; Neuromuscular; Range of motion; Surgery; Therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The corresponding author (Edward K Rodriguez) is an associate editor of BMC Musculoskeletal Disorder. EKR, AN, and MWG are co-inventors on a patent application submitted to the USPTO on the use of human relaxin-2 as a treatment for arthrofibrosis. The patent application is available for licensing.
Figures

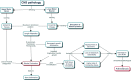

References
-
- Johnson ER, Fowler WM, Lieberman JS. Contractures in neuromuscular disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992. 10.5555/uri:pii:000399939290149Q. - PubMed
-
- Larkindale J, Yang W, Hogan PF, Simon CJ, Zhang Y, Jain A, et al. Cost of illness for neuromuscular diseases in the United States. Muscle Nerve. 2014. 10.1002/mus.23942. - PubMed
-
- Purves D, Augustine G, Fitzpatrick D, Katz L, LaMantia A-S, McNamara J, et al. Neuroscience. 2nd ed. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

